The first recorded use of the term SEO is dated back to 1997.
This means as a discipline SEO has been around for 26+ years, unlike conversion rate optimization, which wasn’t a thing until 2006.
For many businesses, one of their initial forays into digital marketing is to start working on their website SEO/optimizing web pages SEO.
Regarding Google’s ranking algorithm, there are hundreds of unknown ranking factors. Still, we’re familiar with three (site speed, content relevancy/quality, and backlinks), and these factors can be negatively affected when an A/B test is launched if it’s not done properly.
In this article, we’ll extensively look at the impact of running A/B tests on SEO, but I’ll start by defining A/B testing in SEO, the importance of A/B testing in SEO, how to run a successful test that doesn’t negatively impact SEO, and examples of some A/B test ideas.
Let’s get started.
What Is A/B Testing In SEO?
A/B testing, also known as split testing, refers to a methodical approach that involves creating variations of specific elements on a webpage and comparing their performance to determine the best option.
SEO testing, aka SEO split testing, allows website owners to experiment with different variant pages of content, design elements, or user interactions to identify which variant leads to improved search engine rankings and user engagement.
The primary purpose of A/B testing in SEO is to optimize a website’s performance in search engine results pages (SERPs) and enhance its overall visibility.
By systematically testing different versions of webpages, SEO professionals can gather empirical data to understand how changes impact search engine rankings, organic traffic, and user behavior. The insights gained from A/B testing can inform website improvements that positively impact SEO metrics.
Moreover, A/B testing allows for continuous experimentation and refinement. As search engine algorithms evolve and user preferences change, A/B testing enables website owners to adapt and optimize their digital presence to meet evolving demands.
Importance Of A/B Testing In SEO
A/B testing offers numerous benefits that contribute to the overall success of SEO efforts. This section will detail the importance of A/B testing and explore its benefits and impact on SEO.
1. Earn buy-in from higher-ups:
A/B testing provides concrete data to support decisions and gain approval from stakeholders. When proposing changes to a website’s design, content, or functionality, having measurable results from A/B tests helps demonstrate the potential impact of those changes. By presenting data-driven evidence of improved SEO metrics, such as increased organic traffic or higher conversion rates, A/B testing can persuade higher-ups to invest in optimization initiatives.
2. Validate important projects:
A/B testing allows website owners to test significant changes, such as website redesigns, new features, or other crucial modifications, before fully implementing them. This validation process is especially crucial in terms of SEO since untested changes may inadvertently impact site load speed, which is a critical factor for search engine rankings. By running A/B tests, webmasters can gather data on how different versions of the website perform, ensuring that only the most effective and optimized versions are rolled out to the public.
3. Save time:
A/B testing enables iterative improvements, preventing the need for major overhauls based on assumptions. Rather than making sweeping changes to a website based on guesswork, A/B testing allows for incremental adjustments and optimizations. By continuously testing and refining different elements, SEO professionals can fine-tune their strategies and make data-driven decisions, saving time and resources in the long run.
4. Reduce bounce rates:
A/B testing can significantly contribute to reducing bounce rates, which is a crucial SEO metric. By optimizing elements like titles, meta descriptions, and page content through A/B testing, website owners can better engage users and encourage them to stay on the site longer. For example, testing different variations of headlines and meta descriptions can help identify the most compelling and relevant messaging, which in turn can increase click-through rates from search engine result pages (SERPs) and decrease bounce rates.
5. Improve user experience:
A/B testing allows for user-centric improvements by testing different layouts, navigation options, or content presentation. Through A/B tests, website owners can gather insights into how users interact with different site versions and make informed decisions to enhance the overall user experience. For instance, testing different layouts can help identify the most intuitive and user-friendly design, improving engagement and satisfaction.
How To Perform A/B Testing The Right Way In SEO
Performing A/B testing in SEO requires adherence to best practices to ensure accurate results and maintain the website’s integrity. This section will outline key considerations and recommendations for conducting A/B tests in SEO.
1. Avoid cloaking:
Transparency is crucial when conducting A/B tests in SEO. It is important to ensure that the different variations being tested are visible to both search engines and users. Cloaking, which involves presenting content different from what is shown to users to search engine bots, should be avoided. Maintaining transparency and consistency in content presentation helps build trust with search engines and ensures accurate indexing and ranking of the website.
2. Use rel=canonical:
Implementing rel=canonical tags correctly is essential during A/B testing to avoid duplicate content issues. When running A/B tests that involve multiple versions of a webpage, it is crucial to specify the canonical version using the rel=canonical tag. This signals to search engines which version of the page should be considered the primary version, preventing potential issues with duplicate content and ensuring that the correct version is indexed and ranked.
3. Opt for 302 redirects:
During A/B testing, using 302 redirects (temporary redirects) rather than 301 redirects (permanent redirects) is often preferable. 302 redirects allow for flexibility and temporary routing of users to different versions of the webpage being tested. Unlike 301 redirects, which indicate a permanent move, 302 redirects ensure that search engines understand that the redirection is temporary and that both page versions should continue to be indexed and evaluated separately.
4. Test length considerations:
Determining the appropriate duration for A/B tests is crucial to obtain reliable and statistically significant results. Test length depends on various factors, including the amount of traffic the website receives and the desired level of confidence in the results. Generally, running tests for too short a period may lead to inconclusive or misleading results, while excessively long tests can delay decision-making and hinder optimization progress. Using statistical significance calculators to estimate the required test length based on the desired confidence level and traffic volume is recommended.
See this: A/B and Split Test Calculator.
5. Minimize duplicate content:
Running A/B tests can result in temporary instances of duplicate content, negatively impacting SEO. To mitigate this issue, several strategies can be employed. One approach is to use the rel=canonical tag, as mentioned earlier, to specify the canonical version of the page. Additionally, using meta robot tags with “noindex” directives for the non-canonical versions can prevent them from being indexed by search engines. This helps avoid penalties associated with duplicate content and ensures that only the desired version of the page is considered for ranking and indexing.
How To Run A Successful A/B Test That Won’t Negatively Impact SEO
Running a successful A/B test requires a well-structured approach. In this section, I’ll provide a step-by-step guide to conducting an effective A/B test that won’t negatively impact SEO.
1. Uncover test opportunities:
To begin, it’s important to discover site issues that can be tested. To do this, you need both qualitative and quantitative user research methods.
Qualitative user research methods – (user interviews, usability testing, surveys, focus groups).
Quantitative user research methods – (analyzing user behavior with analytics tools).
Employing both research methods help you uncover issues on your site that can be tested and improved on.
Doing this also ensures your A/B test pipeline is full of ideas so you can keep testing.
2. Prioritize testing ideas:
Once you have a list of testing ideas, it’s essential to prioritize them based on their potential impact. Look for patterns in user feedback and behavior to identify common pain points or opportunities for improvement. Consider the potential impact on SEO metrics, user experience, conversion rates, or other relevant factors. By weighing the potential impact of each idea, you can prioritize testing ideas to focus on those with the highest potential for positive results.
3. Create a hypothesis:
A clear hypothesis is crucial for conducting an A/B test. Formulate a hypothesis that clearly states the expected impact of the change you plan to test. A well-structured hypothesis includes an assertion about the change, the expected outcome, and the user segment that is expected to benefit. For example, “By changing the call-to-action button color to green on the checkout page, we expect to increase conversion rates for first-time users by 10%.”
4. Implement the test:
When implementing the A/B test, setting it up correctly is important to ensure accurate results. Create two or more variants (A and B) representing the tested versions. Use reliable A/B testing tools to allocate traffic to the variants randomly and evenly. Ensure that the test runs simultaneously for all users to avoid time-based biases. Implement the changes accurately and monitor the technical aspects to ensure smooth functionality and proper data tracking.
5. Post-test analysis:
When your test is completed, it’s now time to evaluate and interpret the results to determine whether the tested variant outperformed the control or the opposite is the case.
If the results show a significant improvement, consider implementing the winning variant. However, if the results are inconclusive or the tested variant did not perform as expected, analyze the insights gained from the test and iterate further.
To do this is simple – adjust the test parameters, refine the hypothesis/ analyze the implementation of the hypothesis or explore other testing ideas based on the data collected.
A/B Testing Ideas You Should Try On Your eCommerce Website
There are several pages on your website where you can run A/B tests, but in this section, I’ll focus on category and product pages.
Category pages are crucial in guiding users through a website’s content and helping them find relevant information efficiently. A/B testing offers an effective method to optimize category pages, enhancing user experience and driving improved SEO performance. This section will provide A/B testing ideas specifically tailored to category pages, focusing on testing layout styles, filter usage, and different ways of organizing content.
1. Testing layout styles:
Layout styles significantly impact how users interact with category pages. By testing different layout styles, website owners can identify the most effective design that enhances user engagement and facilitates content discovery. Some A/B testing ideas for layout styles on category pages include:
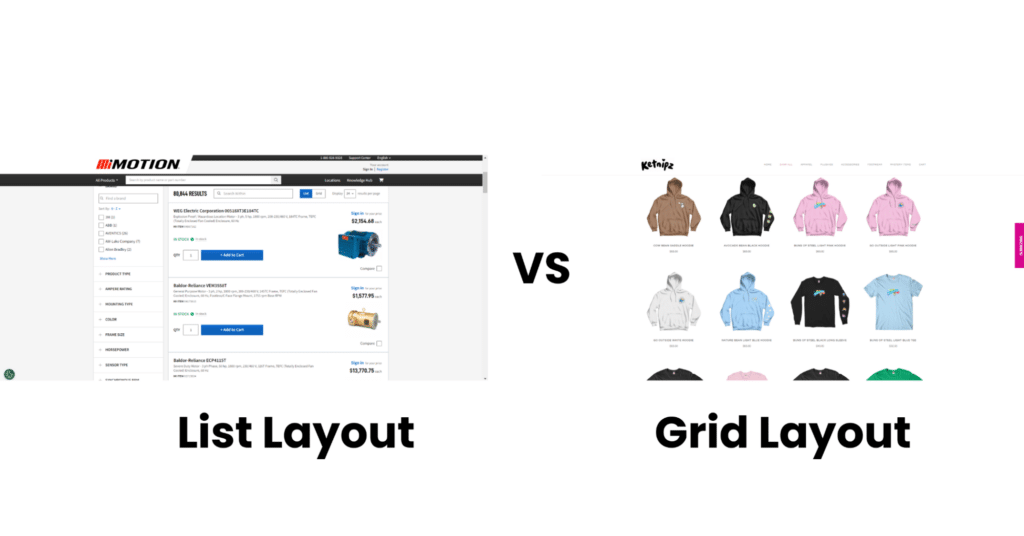
- Grid view vs. list view: If your category pages currently operate a grid view system, you can design a variation with a list view layout to see which one your site visitors prefer. Measure metrics such as click-through rates, time spent on the page, and conversion rates to determine which layout style leads to better user engagement and higher conversion rates.
2. Testing filter usage:
Filters play a vital role in helping users refine their search and narrow down their options on category pages. A/B testing different filter options and their placements can improve user experience and increase conversion rates. Consider the following A/B testing ideas related to filter usage:
- Horizontal vs. vertical filters: Compare the performance of horizontally displayed filters (across the top or bottom of the page) versus vertically displayed filters (typically on the left-hand side). Analyze user engagement metrics and conversion rates to determine which filter placement is more effective in guiding users and facilitating their search process.

Product pages serve as crucial touchpoints for users in their decision-making process.
With A/B testing, you can optimize product pages, enhance user experience, increase conversions, and drive improved SEO performance.
1. A/B testing pricing strategies:
Pricing plays a significant role in user perception and purchase decisions. A/B testing different pricing strategies can help determine the most effective approach to maximize conversions and revenue. Consider the following A/B testing ideas for pricing on product pages:
- Single pricing vs. Breaking down the price with interest: Test the effect of offering a single pricing option vs a single pricing option and the option of breaking down the payment into installments. Assess user behavior, conversion rates, and revenue generated to determine which pricing approach leads to higher customer engagement and increased conversions.

2. Comparing images vs. videos:
Visual content plays a vital role in showcasing products and engaging users. A/B testing different media formats, such as images and videos, can provide insights into which format drives better user engagement and influences purchase decisions. Consider the following A/B testing ideas for images and videos on product pages:
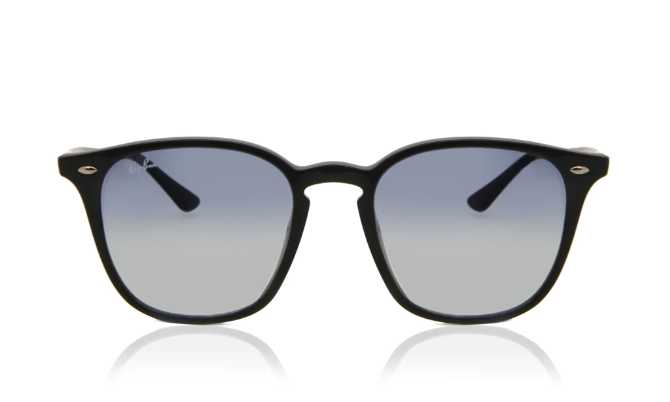
- Static images vs. product videos: Compare the performance of displaying static product images versus incorporating product videos. Evaluate metrics such as time spent on the page, click-through rates, and conversion rates to understand which format better captures user attention and effectively showcases the product’s features and benefits.
Here is a static image example of a competing eyewear retailer;

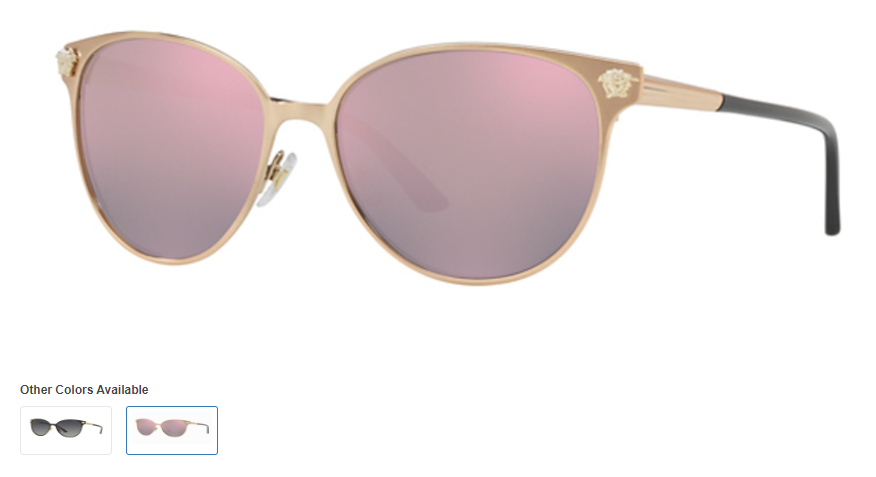
- Multiple images vs. 360-degree views: Test the impact of presenting multiple product images compared to providing 360-degree views of the product. Measure user engagement, click-through rates, and conversion rates to determine which approach enhances user understanding and product visualization, leading to increased conversions.
Here’s an example of a 360 view of a product;

Here’s an example of a product page with just static eyeglass images;

3. Exploring upselling and cross-selling techniques:
Upselling and cross-selling techniques can effectively increase average order value and improve the overall shopping experience. A/B testing different approaches to upselling and cross-selling can help identify the most successful strategies for product pages. Consider the following A/B testing ideas for upselling and cross-selling:
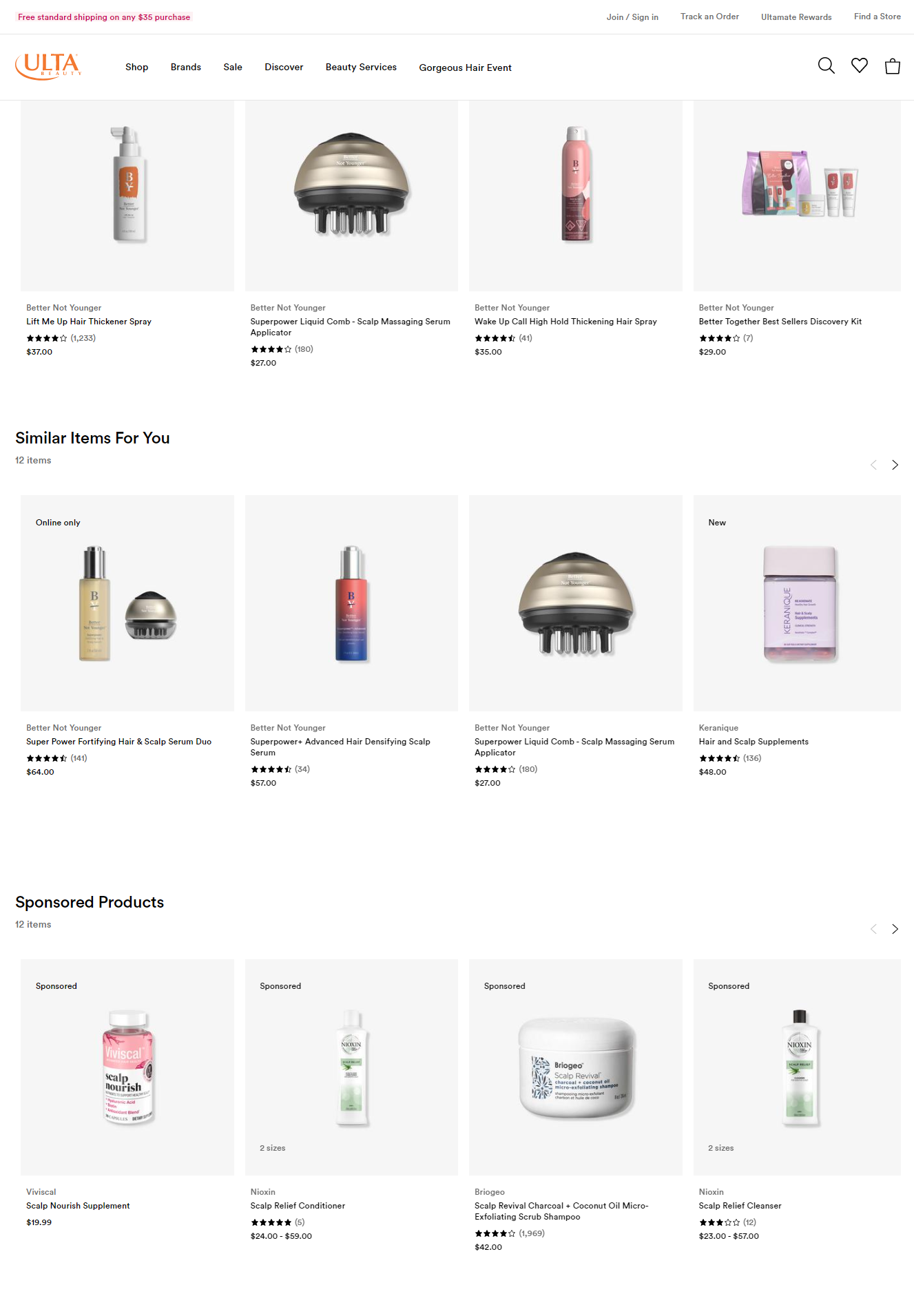
- Try different names for the upselling section: On most ecommerce sites, the upselling/cross-selling section is named related products/customer favorites and other titles. You can switch out those names and try new ones.
This example from Ultamate is unique, and that’s because they used different naming conventions and have upto 3 upselling/cross-selling sections per product page.
Final Thoughts
To ensure your website doesn’t lose significant SEO rankings when you conduct A/B tests, it’s important you follow the tips and best practices outlined in this article.
Ensure to always opt for 302 redirects, minimize duplicate content, and use rel = canonical.
Do this, and you’ll always be on the safe side of search engines.



