Everyone views life through different lenses.
This is why a boomer might prefer a more laid-back holiday plan where they don’t have to stress much, but a Gen Z signs up to climb Mt Everest.
The fact is, psychographic segmentation is a big part of how we live our lives and interact with the surrounding environment.
Marketers use psychographic segmentation to attract customers who share the same beliefs and perceptions with how they project their brand/business.
In this article, I’ll define what psychographic segmentation is, highlight its benefits, highlight how to collect psychographic data and share some real-world examples.
Let’s get started.
What Is Psychographic Segmentation?
Psychographic segmentation is a powerful tool by which marketers categorize individuals based on their psychological and lifestyle characteristics.
This includes factors such as values, interests, personality traits, and buying habits.
It goes beyond traditional demographic segmentation data like age, gender, and location to delve deeper into understanding consumer behavior and preferences.
By employing psychographic segmentation, businesses gain a comprehensive view of their target audience, allowing them to tailor their marketing strategies precisely.
Rather than making assumptions solely based on demographics, they can connect more profoundly, resonating with consumers on shared values and interests.
The following sections will explore how this approach can significantly drive engagement and enhance marketing effectiveness.
Difference Between Psychographic Segmentation and Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation and psychographic segmentation are two distinct approaches to understanding consumer behavior, each offering unique insights into audience engagement.
Behavioral Segmentation:
As the name suggests, behavioral segmentation centers on consumers’ actions and interactions with a product or service. It involves analyzing how individuals use a product, how often they use it, and their purchasing patterns.
This approach looks at the observable behaviors of consumers, such as their buying history, brand loyalty, and response to marketing campaigns.
Businesses can make data-driven decisions on product development, pricing strategies, and marketing tactics by dissecting these actions. For example, if an e-commerce platform notices that a group of customers frequently makes high-value purchases, they can tailor exclusive offers to reward and retain these loyal buyers.
Psychographic Segmentation:
On the other hand, psychographic segmentation delves deeper into the internal psychological factors that influence consumer behavior. It focuses on understanding consumers’ values, beliefs, interests, personality traits, and lifestyles.
This approach goes beyond the “what” of consumer actions to uncover the “why.” By identifying shared values or interests within a target audience, businesses can create marketing campaigns that resonate on a personal level.
For instance, if a cosmetics brand recognizes that a segment of its audience values eco-friendly products and sustainable living, it can develop and promote products that align with these values, effectively engaging this particular group.
While behavioral segmentation relies on tangible and observable behaviors, psychographic segmentation explores the underlying motivations, thought processes, and emotional connections that drive consumers.
Both approaches are valuable tools in crafting effective marketing strategies, but they address different dimensions of consumer behavior and can be used in conjunction to create comprehensive marketing campaigns that drive engagement and resonate with the target audience.
What Are The Benefits Of Psychographic Segmentation?
1. Deeper Understanding of Customer Needs:
Psychographic segmentation allows businesses to uncover the hidden motivations and desires that underlie consumers’ buying decisions. By delving into their values, interests, and lifestyles, companies can gain profound insights into what truly drives their audience.
This understanding empowers them to create products and services that align better with customers’ values and preferences, resulting in offerings that are not only attractive but also resonate deeply with their target market.
2. Increased Customer Loyalty:
Crafting messages and marketing strategies that resonate with customers’ values and beliefs goes beyond transactional relationships. It fosters a lasting sense of loyalty.
When customers feel that a brand understands and shares their values, they are more likely to develop a strong emotional connection with that brand. Moreover, tailoring offerings to specific psychographic segments can lead to even stronger emotional connections, translating into repeat business.
Customers who find products and services that align with their lifestyle are more inclined to become loyal, returning customers.
3. Improved Targeted Marketing:
Psychographic segmentation empowers businesses to move away from generic marketing approaches. Instead, it enables them to tailor content and marketing efforts to the specific psychographic segments they serve.
This approach substantially increases the effectiveness of marketing campaigns by addressing consumers’ distinct needs and interests.
As a result, engagement rates and conversion rates are often higher as the marketing message resonates more deeply with the intended audience.
4. Competitive Advantage:
The business landscape is competitive, and understanding customers on a deeper level is more paramount than ever.
Businesses that employ psychographic segmentation gain a significant advantage by delivering more relevant solutions and experiences. This sets them apart from competitors who may rely solely on demographic data.
Enhanced customer experiences, driven by psychographic insights, frequently lead to a distinct competitive edge. When customers feel understood and valued, they are more likely to choose one brand over another, ultimately boosting market share and profitability.
Variables of Psychographic Segmentation
1. Personality:
Psychographic segmentation based on personality traits involves categorizing individuals according to characteristics like introversion, extroversion, adventurousness, and more.
Brands can utilize this information to tailor their messaging to actively resonate with specific personality types.
For instance, campaigns can be crafted to engage introverted individuals by highlighting the comfort and relaxation aspects of a product, whereas, for adventurous personalities, marketing messages might emphasize excitement and novelty.
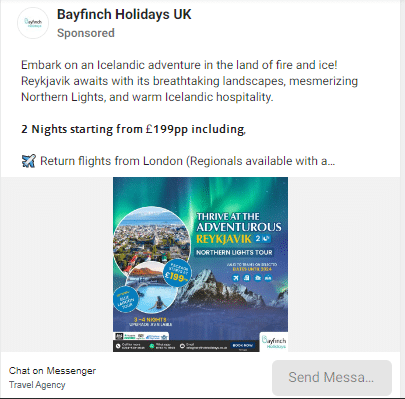
See this example from BayFinch Holidays (a travel agency). Their ads clearly target those with a spice of adventure in them.
2. Attitude:
Attitude-based segmentation delves into customers’ attitudes and opinions regarding products, brands, or social issues.
This approach is proactive in nature, as it involves actively identifying and analyzing these attitudes to inform marketing strategies.
By aligning campaigns with consumers’ beliefs, businesses can foster stronger connections. For example, if a significant portion of the target audience holds environmentally conscious views, a brand can take an active stance on sustainability and weave eco-friendly messaging into its branding efforts.
See this example from Seventh Generation, this TV commercial targets the environmentally conscious.

3. Lifestyle:
Lifestyle segmentation takes into account the multifaceted aspects of people’s lives, considering their hobbies, interests, daily routines, and cultural preferences.
This dynamic approach enables companies to actively position products and services in contexts that closely align with consumers’ lifestyles.
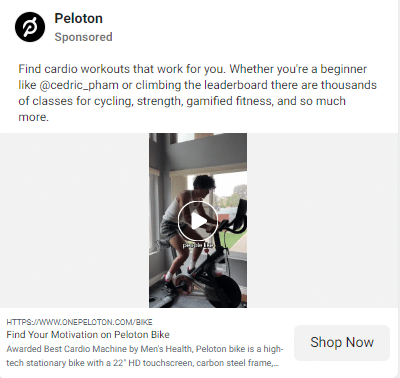
For instance, a fitness brand can proactively target individuals with active and health-conscious lifestyles by portraying its products as essential to their daily routines.
Peloton is great at this.
4. Social Status:
Social status segmentation actively acknowledges consumers’ economic standing, social class, and aspirations.
Companies that engage in this form of segmentation can proactively customize their offerings to appeal to distinct social status groups.
This may involve targeting luxury products to affluent segments while simultaneously proactively offering budget-friendly options to cater to price-sensitive customers.
See this Dior Ad (note the image used and the choice of words in the copy).

4. Activities, Interests, Opinions (AIOs):
AIOs provide a comprehensive, actively curated view of customers’ hobbies, preferences, and viewpoints. Armed with this data, companies can proactively tailor their marketing strategies based on shared activities and interests.
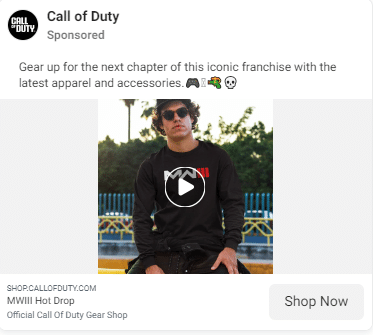
For instance, a tech company can take an active approach by targeting a segment of customers who share a passion for gaming.
By creating specialized gaming products and content that actively resonate with this audience’s interests, the brand can actively engage and captivate this specific group of consumers.
Call of Duty does this so well.
How To Collect Psychographic Data
1. Surveys and Questionnaires:
Surveys and questionnaires actively engage your audience to provide insights into their psychographics. Craft well-structured inquiries, such as:
- “What values do you consider most important in your life?”
- “How do you spend your leisure time?”
- “What are your opinions on [relevant industry topic]?”
Distribute them actively through various channels like email, social media, or your website. Encourage active participation by offering incentives or making the process as effortless as possible.
2. Social Media Analysis:
Explore the wealth of information available on social media platforms. Monitor conversations, comments, and interactions related to your brand, products, or industry.
Extract insights about consumer attitudes, preferences, and behaviors from these active online conversations.
You can use social media monitoring tools such as Hootsuite, Mention, or Brandwatch to actively track brand mentions, hashtags, and discussions relevant to your industry or products.
3. Website and App Analytics:
Track user behavior on your website or app. Utilize analytics tools like Google Analytics to understand how visitors navigate your digital space.
Identify patterns such as which pages they frequently visit, what content they engage with, and the products or services they actively show interest in.
With Google Analytics, you can set up goals and funnels to track specific actions and actively segment data by demographics and interests.
4. Customer Interviews and Focus Groups:
Engage with your customers through interviews and focus groups. Ask open-ended questions that encourage them to share their thoughts, values, and experiences. For example:
- “Can you describe your recent purchase decision and what influenced it?”
- “What social or environmental issues do you care most about?”
The insights gleaned from these conversations are invaluable for shaping psychographic profiles.
5. Third-party Data Sources:
Actively explore third-party data sources that offer psychographic information about your target audience.
Look for data sources that align with your industry and customer demographics. For example, you can purchase market research reports that provide insights into consumer attitudes and lifestyles within your niche.
Real-World Examples of Psychographic Segmentation
1. Patagonia
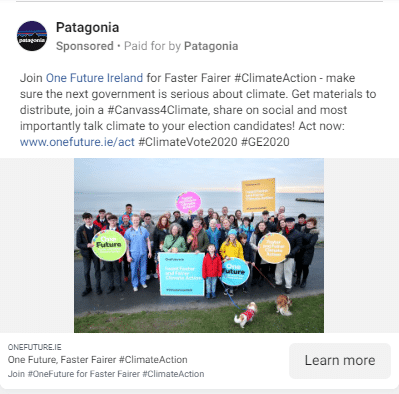
This brand designs clothes and gears for the environmentally conscious individual i.e. folks who care about the environment, protecting it, and living in it.
Their ads speak to this effect.
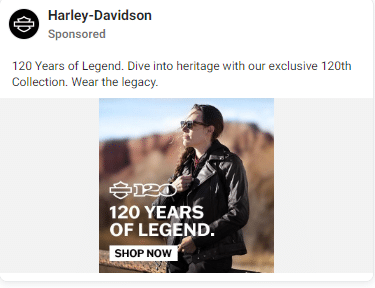
2. Harley-Davidson
This motorcycle brand taps into the psyche of riders, including their image, attitude, and bucket-list trips.
It helps them see themselves as they want to be perceived.
Their campaigns agree with this (notice the copy and imagery used).
Final Thoughts
To consistently stay ahead of your competitors, you need to utilize psychographic segmentation for your business. This way, your campaigns, ads, and sales-led efforts will convert better. Successfully doing thisT will also reflect in increased retention and customer lifetime value thanks to repeat purchases.



