For many businesses, their market segmentation starts and ends with knowing their average customer’s location, gender, age, role, etc.
This is mostly a bit of demographic and geographic market segmentation. To drive more conversions from campaigns, ads, and emails, there’s a need for a different type of segmentation.
Enter behavioral segmentation.
In this article, we’ll define what behavioral segmentation means, benefits of behavioral segmentation, types of behavioral segmentation, real examples of behavioral segmentation etc.
Let’s dive in.
What Is Behavioral Segmentation?
Behavioral segmentation is a marketing concept that involves categorizing consumers based on their behaviors and actions rather than relying solely on traditional demographic factors like age, gender, or income.
This approach recognizes that consumer behaviors, such as purchasing habits, usage patterns, brand interactions, and response to marketing campaigns, can provide deeper insights into their motivations and preferences.
Traditional marketing strategies often focused on demographic information, assuming that individuals within the same demographic group had similar preferences.
However, this approach proved to be limited in its ability to predict and influence consumer behavior accurately.
This is where behavioral segmentation steps in, revolutionizing the way marketers approach their strategies.
By grouping consumers based on their behaviors and interactions with a brand, product, or service, marketers gain a more nuanced understanding of their target audience.
This understanding goes beyond surface-level demographics and dives into the psychology of purchase decisions. For instance, behavioral segmentation allows marketers to identify:
Purchase Patterns: Marketers can discern whether consumers are frequent purchasers or occasional buyers. This insight helps tailor marketing efforts to each group’s specific needs.
Product Usage: Understanding how often and how extensively consumers use a product or service helps in crafting targeted messaging and product improvements.
Brand Loyalty: Behavioral segmentation highlights customers who consistently choose a particular brand, aiding in loyalty program customization and retention strategies.
Response to Marketing Campaigns: Marketers can evaluate which segments respond most positively to specific marketing campaigns. This knowledge enables the creation of campaigns that resonate better with different groups.
Abandoned Carts and Engagement: Identifying segments that frequently abandon their online shopping carts allows marketers to address pain points and design smoother checkout processes.
Channel Preferences: Knowing which channels consumers prefer for interactions and purchases guides the allocation of marketing resources effectively.
Behavioral segmentation’s true power lies in its ability to enhance engagement and conversion rates significantly.
When marketers understand the psychology behind different consumer behaviors, they can craft personalized experiences that align with those behaviors.
This alignment creates a sense of relevance and resonance, which can lead to improved engagement and conversion rates.
What Are The Benefits Of Behavioral Segmentation?
1. Enhanced Personalization:
Personalization has become the cornerstone of effective marketing.
Behavioral segmentation elevates personalization to an art form by allowing marketers to create tailored experiences for each segment.
Whether it’s sending personalized product recommendations based on previous purchases or addressing pain points specific to each group, this level of customization fosters a stronger emotional connection between consumers and brands.
Businesses like Amazon, Netflix, Spotify, Apple Music do this so well by using your previous purchase/search behavior to recommend products to you.
2. Precise Targeting:
One-size-fits-all marketing is a relic of the past. Behavioral segmentation equips marketers with a laser-focused approach, ensuring that messages and offers reach the right people at the right time.
By identifying consumers who exhibit certain behaviors, such as frequent purchases or abandoned carts, marketers can fine-tune their strategies to address the unique needs of each segment, thereby minimizing wasted resources.
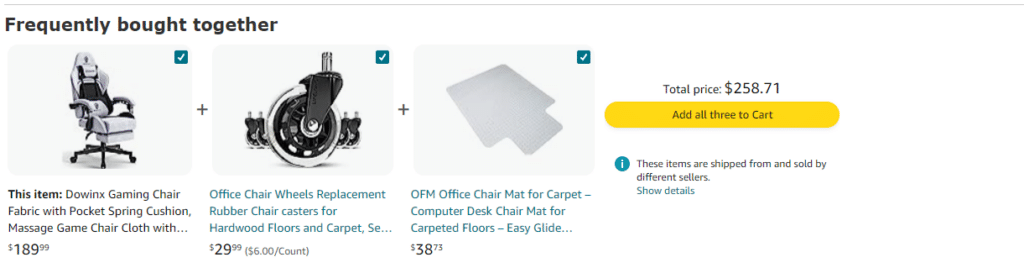
Here’s an example of how Honey Teas retarget their frequent purchasers with email.
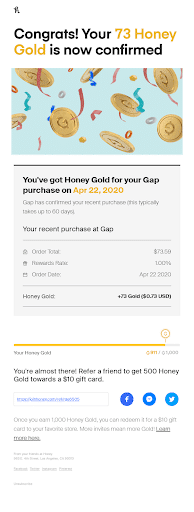
3. Improved Customer Experience:
Understanding the intricacies of consumer behaviors paves the way for an elevated customer experience.
When businesses can anticipate customer needs and preferences, they’re better equipped to provide seamless interactions and timely solutions.
This could mean suggesting complementary products, offering proactive customer support, or even tailoring website interfaces to match individual preferences.
I’m a big fan of romantic songs, so it made sense when Spotify made this list for me:
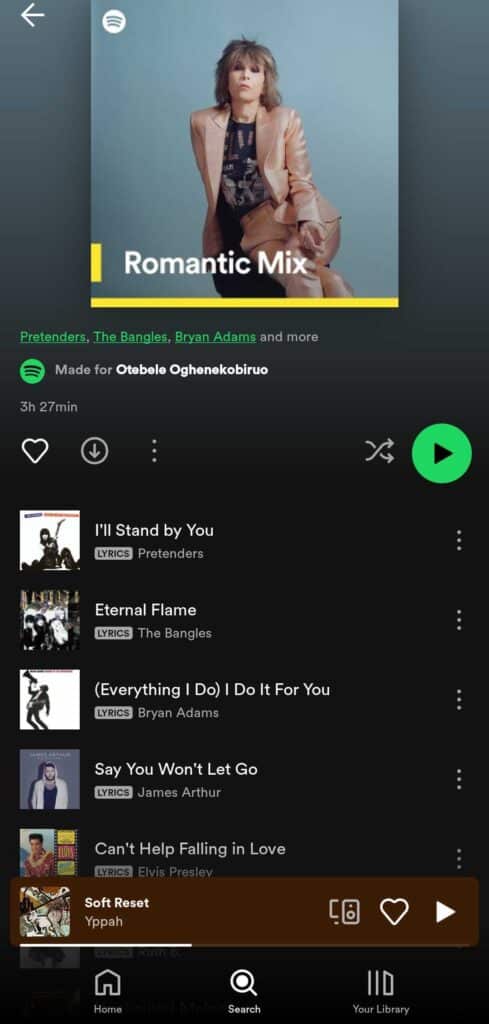
4. Tailored Product Development:
In the ever-evolving world of product innovation, behavioral segmentation provides a compass.
By understanding how consumers use products and what they seek, businesses can refine existing offerings and develop new ones that cater precisely to these needs.
This ensures that resources are allocated where they are most likely to yield success.
5. Effective Cross-Selling and Upselling:
The art of suggesting relevant complementary products is elevated with behavioral segmentation.
Analyzing consumer behaviors, marketers can determine which products are often purchased together. This insight facilitates strategic cross-selling and upselling, driving higher average transaction values and increasing revenue.
See this example from Amazon:
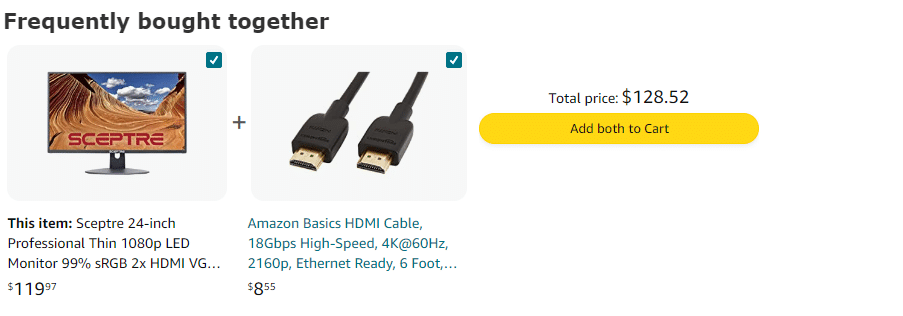
6. Optimized Marketing Campaigns:
Generic marketing campaigns typically fall flat.
Behavioral segmentation injects vitality into campaigns by enabling marketers to craft messages that align with each segment’s behaviors and preferences.
This leads to campaigns that resonate on a personal level, capturing attention and driving action.
Exploring 7 Main Types of Behavioral Segmentation
1. Purchase Behavior:
Understanding how consumers make purchase decisions is fundamental to any marketing strategy.
This type of segmentation categorizes consumers based on their buying patterns. These patterns can encompass factors like the frequency of purchases, the average order value, and the types of products or services purchased.
Purchasing behavior can be broken down into 4 main categories:
- Complex: Some consumers engage in an extensive decision-making process for high-involvement purchases, requiring detailed research and comparisons. Marketers must provide comprehensive information and expert guidance to aid these individuals in making informed choices.
- Variety-Seeking: Certain consumers actively seek novel experiences and products, often showing less brand loyalty. Marketers can capture their attention by highlighting new offerings, limited-time deals, and unique experiences.
- Dissonance-Reducing: After making a purchase, some consumers experience doubt and seek reassurance. Marketers can alleviate post-purchase dissonance by offering warranties, support, and content that addresses concerns.
- Habitual: Routine purchases, driven by familiarity, form the basis of this behavior. Marketers can cultivate brand loyalty through strategies like loyalty programs and subscriptions to maintain consistent engagement.
By identifying different purchasing behaviors, marketers can tailor promotions, discounts, and product recommendations to each segment’s buying habits.
2. Occasion and Timing:
Consumer behavior typically shifts based on occasions and timing.
This segmentation capitalizes on this by grouping consumers based on when they are most likely to purchase.
Whether it’s holiday shopping, back-to-school promotions, or seasonal trends, marketers can design campaigns that tap into consumers’ psychological triggers during these specific times, boosting engagement and conversions.
There are 3 main categories here:
- Universal occasions — Purchasing patterns that apply to most of your customers or target audience within a certain demographic (holidays, seasonal events, etc.)
- Recurring-personal occasions — Purchasing patterns for an individual customer that repeat consistently over some time based on their personal life (birthdays, anniversaries, regular monthly purchases, etc.)
- Rare-personal occasions — Purchasing patterns for an individual customer that are more irregular, spontaneous, and difficult to predict (weddings, road trips, etc.)
3. Benefits Sought:
Consumers don’t just buy products; they seek solutions and benefits. This segmentation revolves around categorizing consumers based on the specific benefits they seek from a product or service.
Some might prioritize convenience, while others focus on cost-effectiveness or luxury. By tailoring messages that address the unique benefits desired by each segment, marketers create messaging that resonates deeply.
Types of benefits sought could include:
- Quality
- Price
- Reviews & feedback
- Other unique selling points (USPs)
In this example by Selfridges, the ”What’s Trending” section of the website allows consumers to make more informed decisions about the best products they can browse and buy with their platform, according to other customers.
Consumers who convert through this section of the website can be segmented into a benefits-driven group.
4. Customer Loyalty:
Customer loyalty is a coveted asset in business. This segmentation distinguishes between various levels of customer loyalty, from occasional purchasers to brand advocates.
Diving deeper into this segmentation, you can divide customers based on their user status. As well as first-time buyers and returning customers, you can also begin to consider prospective customers (who need more convincing, or more incentive to buy), and customers who may want to return after previously leaving the ‘loyal customer’ category.
By nurturing relationships with loyal customers through personalized offers, exclusive content, and rewards, marketers can strengthen brand affinity and drive repeat business.
In this example, we see Nike rewards loyal customers are rewarded with exclusive rewards:

5. Customer Journey Stage:
The path to purchase is a multi-step process, and understanding where consumers stand along this journey is crucial.
This segmentation aligns marketing efforts with the different stages consumers go through, such as awareness, consideration, and decision-making.
Marketers guide consumers toward conversion by delivering relevant content and offers at each stage more effectively.
6. Engagement:
Engaged consumers are more likely to convert into customers.
This segmentation examines how consumers interact with a brand’s marketing materials—whether they open emails, click on links, or actively participate in online communities.
Marketers can tailor content and messages by categorizing consumers based on their engagement levels to capture and retain attention.
7. Customer Satisfaction:
Customer satisfaction is the linchpin of repeat business and positive word-of-mouth.
This segmentation measures consumer satisfaction levels and divides them into segments based on their feedback and experiences.
This information enables businesses to address concerns, celebrate successes, and design strategies to elevate overall satisfaction.
Real-World Examples of Behavioral Segmentation
BabyCentre UK
BabyCentre UK is Part of the Johnson & Johnson multinational corporation.
A pregnancy and childcare resource located in the United Kingdom.
The company uses a Facebook Messenger app to suggest personalized advice and make targeted recommendations based on the input that it receives from the user through a series of questions and answers.
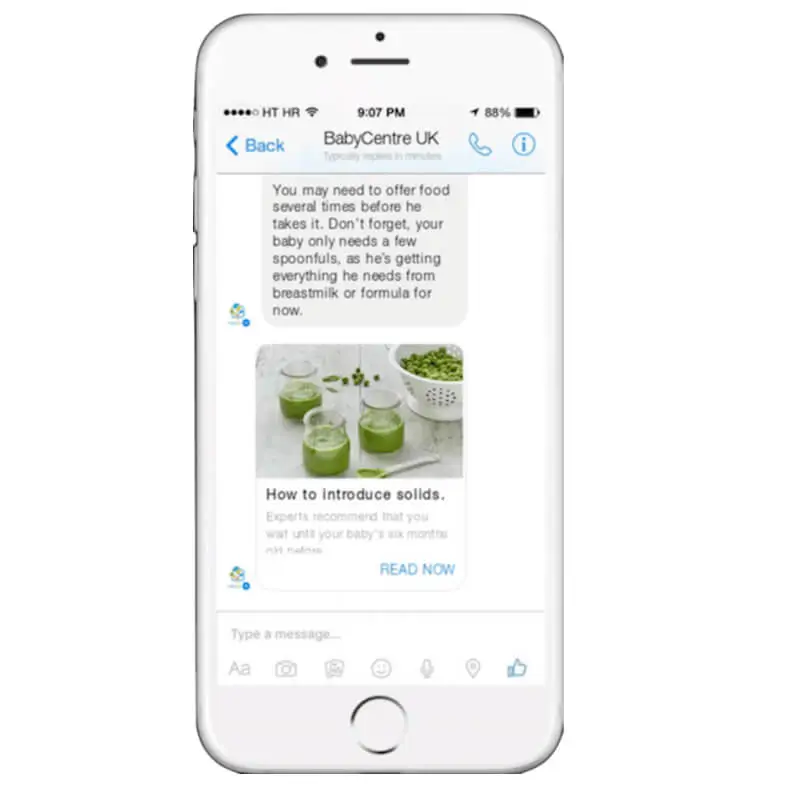
For example in the promotional images above, when the parent selects weaning as the problem they are encountering, the BabyCentre app engages the user by giving them a list of signs to look out for, as well as then suggesting recipes for when the child is ready for solid food.
This tailored experience provides BabyCentre with actionable data that it can use to segment the user by the information obtained through their selections: For example, their child falling into an age category that experiences weaning. Categorizing by this data can help target the customer with repeat, relevant information – such as recipe guides or other helpful advice.
When Babycentre investigated what drove the highest levels of traffic to its website – the chatbot or email marketing – it revealed that the messenger bot recorded a read rate of 84% and click-through rate (CTR) of 53%.
Together, the stats made for an overall engagement rate that was 1,428% higher than its email funnel, adding further evidence to how effective segmentation can be when categorized correctly.
Olay
American skincare brand Olay used benefits sought behavioral segmentation when creating its Skin Advisor.
The artificial intelligence beauty tool collects data from customers by asking them five to seven quick questions about their skin. The advisor then reveals the true age of the customer’s skin, and recommend products accordingly.
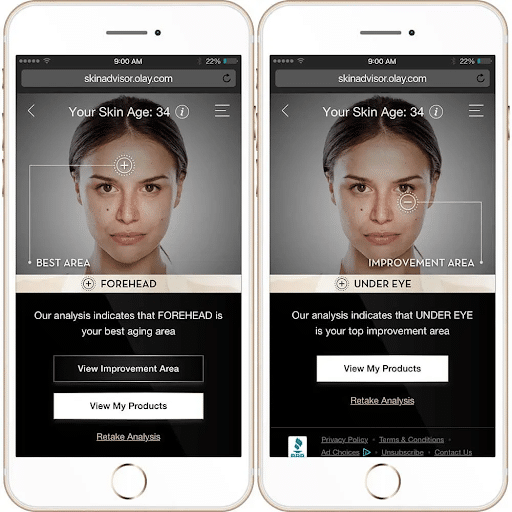
By asking the customer questions based around their skincare routine, and their preferences, Olay can collate data that can influence its product development, allowing the brand to bring out products that are most sought after and most relevant to their customers.
For example, through its Skin Advisor app, Olay gleaned that a large percentage of its consumer base wanted fragrance free products. Originally, these products were not even considered by Olay’s development team, but they were then able to be actioned for manufacturing.
Olay did the same when data from the Advisor revealed that many customers were seeking Retinol based products, and the subsequent lack of Retinol products in its range was contributing to the brand losing custom.
In response, Olay released Retinol 24 which has gone on to be one of the brand’s best-selling products and which helped to completely transform their sales.
Final Thoughts
To gain an edge over your competitors, you need to employ behavioral segmentation for your business. This way, your campaigns and marketing strategies will convert better, and you can tailor the right offers/messages to the right segment of your audience (increasing loyal customers). This will also reflect in increased retention and customer lifetime value thanks to repeat purchases.



