Businesses are always on the lookout for how to generate more demand for their products, reduce customer acquisition costs, and churn.
One of the effective ways under market segmentation to do this is by geographic segmentation.
The fact is geographic segmentation redefines what we know and understand to be personalization.
This is because; geographic segmentation organizes your audience into groups based on factors like region, language, cultural preferences, etc.
This type of segmentation allows for more niche targeting and effective marketing efforts.
In this article, I’ll define what geographic segmentation is, the benefits, variables of geographic segmentation, and real-world examples.
Let’s get started.
What Is Geographic Segmentation?
Geographic segmentation is a strategic approach in marketing that involves categorizing and targeting audiences based on their geographical location.
This segmentation method recognizes the varying preferences, behaviors, and needs of consumers in different regions or locations.
By tailoring marketing strategies and campaigns to specific geographic segments, businesses can effectively connect with their audience on a more personalized level.
What Are The Benefits Of Geographic Segmentation?
1. Easy to Implement
Geographic segmentation offers a streamlined approach to campaign planning and execution.
It simplifies the process by categorizing audiences based on location, making it easier to tailor content and strategies to specific regions.
The beauty of this approach lies in its compatibility with existing strategies; minimal adjustments are required to integrate location-based insights into marketing efforts.
Marketers can start small, target a few key regions, and gradually expand their efforts as they gain insights and refine their approach.
For instance, consider the case of a local bakery that wanted to enhance its marketing efforts.
By using geographic segmentation, they identified the neighborhoods with the highest demand for their products. They started by customizing their promotions for these areas, leading to increased foot traffic and sales without disrupting their overall business strategy.
Tips for Gradual Implementation:
- Begin by analyzing your customer data to identify regions with higher engagement.
- Tailor messaging and promotions for a few key regions initially.
- Monitor results and refine your approach based on performance data.
- Gradually scale up your geographic segmentation efforts as you gather more insights.
2. Higher Product Relevancy
Geographic segmentation ensures that products and offerings align with local preferences and cultural norms. This level of customization is crucial for resonating with consumers on a deeper level.
For example, a global fast-food chain might modify its menu to include region-specific dishes or ingredients that are popular in certain areas. This boosts customer satisfaction and fosters a sense of connection and loyalty to the brand.
KFC exemplifies this. They partnered with Yum China to introduce Chinese breakfast products, such as congee, pancakes, rice rolls, and bean curd pudding.
In January 2021, KFC launched hot, dry noodles at more than 100 stores in Wuhan, making it the first noodle product since entering China.
In September 2021, after launching a series of locally inspired snacks in different cities, hot, dry noodles became the first regional menu item to launch at KFC stores nationwide as a Limited Time Offer (“LTO”).
Over 1 million bowls of hot, dry noodles were sold within a week of launching, becoming KFC’s best-performing LTO breakfast item in the past three years.

By tailoring products to local tastes, businesses can experience higher sales and improved customer retention rates.
When customers find products that resonate with their preferences, they are more likely to return and become loyal patrons.
3. Improved Advertising Effectiveness
Targeted advertisements resonate more effectively with local audiences compared to generic ads. For instance, an advertisement for winter clothing might not appeal to audiences in warmer climates.
By delivering geographic-specific messaging, companies can create emotional connections by addressing local concerns, needs, and aspirations.
Here’s a post on X (an observation by a football fan):
Today I learned that stadiums can have different ads depending on channel and country. pic.twitter.com/qfgGTK7tu4
— Oliur (@UltraLinx) July 4, 2021
See this YouTube Video on how Mcdonalds’ target folks in different regions.
Note: Localized advertisements also lead to efficient allocation of ad spend. When ads are tailored to audiences more likely to convert, the return on investment increases significantly.
4. Higher Customer Satisfaction
Personalized content based on location enhances user experience and makes customers feel understood and valued.
By delivering campaigns that reflect customers’ local context, brands can drive better customer satisfaction. This positive experience not only contributes to the brand’s reputation but also encourages word-of-mouth referrals, further expanding the brand’s reach.
Imagine a travel agency that customizes its marketing messages to showcase destinations relevant to each customer’s geographic location. This strategy promotes positive engagement and generates a sense of appreciation among customers who feel that the brand truly cares about their preferences.
5. Provides Market Opportunities
Geographic segmentation helps identify untapped market opportunities. Businesses can uncover regions with specific needs or preferences that align with their offerings by analyzing data.
For instance, a tech company might discover demand for its products in a region that has recently undergone digital transformation.
Being a first-mover in a new market segment provides a competitive advantage.
Companies that effectively utilize geographic targeting can establish themselves as pioneers, capturing the attention and loyalty of a previously underserved audience.
Conducting Market Research for Opportunities:
- Analyze demographic, economic, and cultural data for different regions.
- Identify gaps between existing market offerings and local needs.
- Tailor products and marketing strategies to fill these gaps and address unmet demands.
6 Types of Geographic Segmentation
1. Location
Segmenting based on physical location forms the cornerstone of geographic segmentation.
This approach acknowledges that different regions have distinct consumer behaviors, preferences, and needs.
When businesses create campaigns and offerings based on user locations, this targeted approach resonates with consumers and demonstrates the brand’s commitment to understanding their local context.
For example, Nike in the US is likely to focus on American football and baseball, while you’re unlikely to see American football or baseball commercials in Europe – you’ll see product ads for Soccer (Football in Europe) instead.
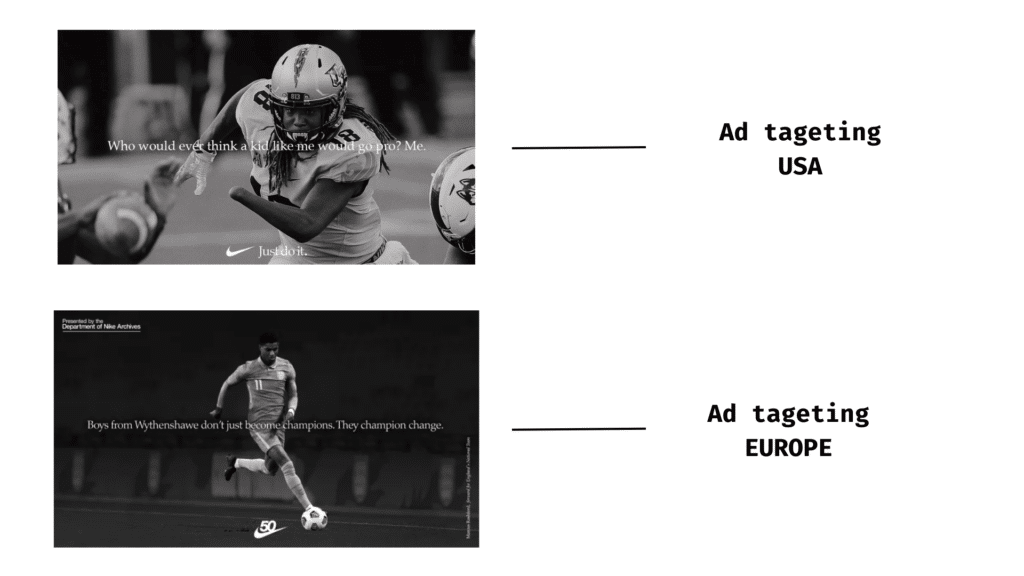
2. Timezone
Timezone-based segmentation recognizes that timing plays a crucial role in effective communication.
Businesses that operate in global markets understand that sending marketing messages at appropriate times maximizes engagement.
For instance, a company hosting a webinar series spanning different continents might schedule sessions when most participants are awake and available.
This approach ensures that the content reaches its intended audience during their active hours, leading to higher participation rates and enhanced interactions.
3. Climate and Season
Adapting campaigns to local climates and seasons showcases a brand’s sensitivity to regional differences.
A boot-making company can leverage climate-based segmentation to promote relevant products. In colder regions, they might craft advertisements featuring winter boots and thick clothes to keep you warm, providing a sense of comfort during chilly months.
This is what Cool Antarctica did:
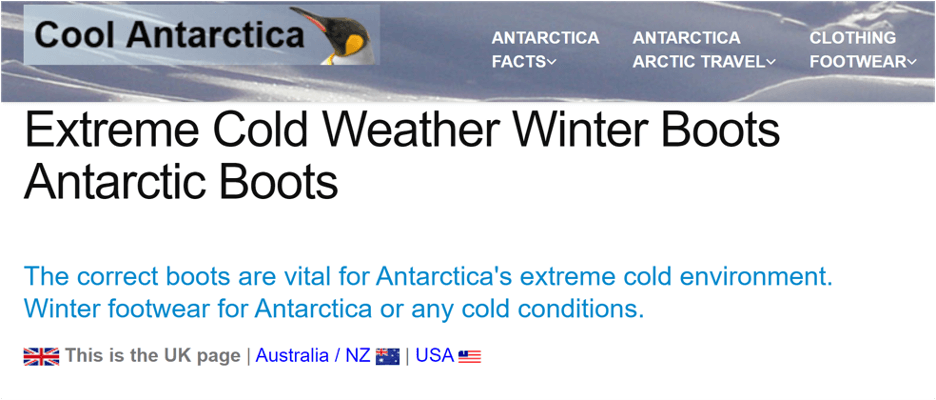
By aligning campaigns with the immediate climate and season, businesses create a relatable and resonant connection with their audience.
4. Cultural Preferences
The significance of understanding cultural nuances in geographic segmentation cannot be overstated.
Brands that take the time to comprehend local customs, traditions, and tastes can effectively tailor their offerings.
In India, McDonald’s doesn’t serve any beef or pork in any form in any of their outlets. Instead of ground beef and pork patties, the McDonald’s menu in India features Indian burgers that are 100% vegetarian.
This is because diets in India have been affected by different religions for centuries.
Hindus don’t eat beef — and the cow is considered sacred. Since the majority of the population follows Hinduism, there’s no beef on McDonald’s’ menu in India. There’s also no pork out of respect for Muslims.
Also, different countries will enjoy different flavors and often have unique items, such as Thailand McDonald’s (Samurai Pork Burger) vs. UK McDonald’s (Mozzarella Dippers).

Such adaptations delight local consumers and demonstrate the brand’s dedication to providing an authentic and culturally relevant experience.
5. Language
Language-based segmentation ensures that communication transcends linguistic barriers.
Brands that offer content in multiple languages cater to a broader audience and foster inclusivity.
Streaming services like Netflix excel in this aspect, providing subtitles and dubbing options in various languages for their content.
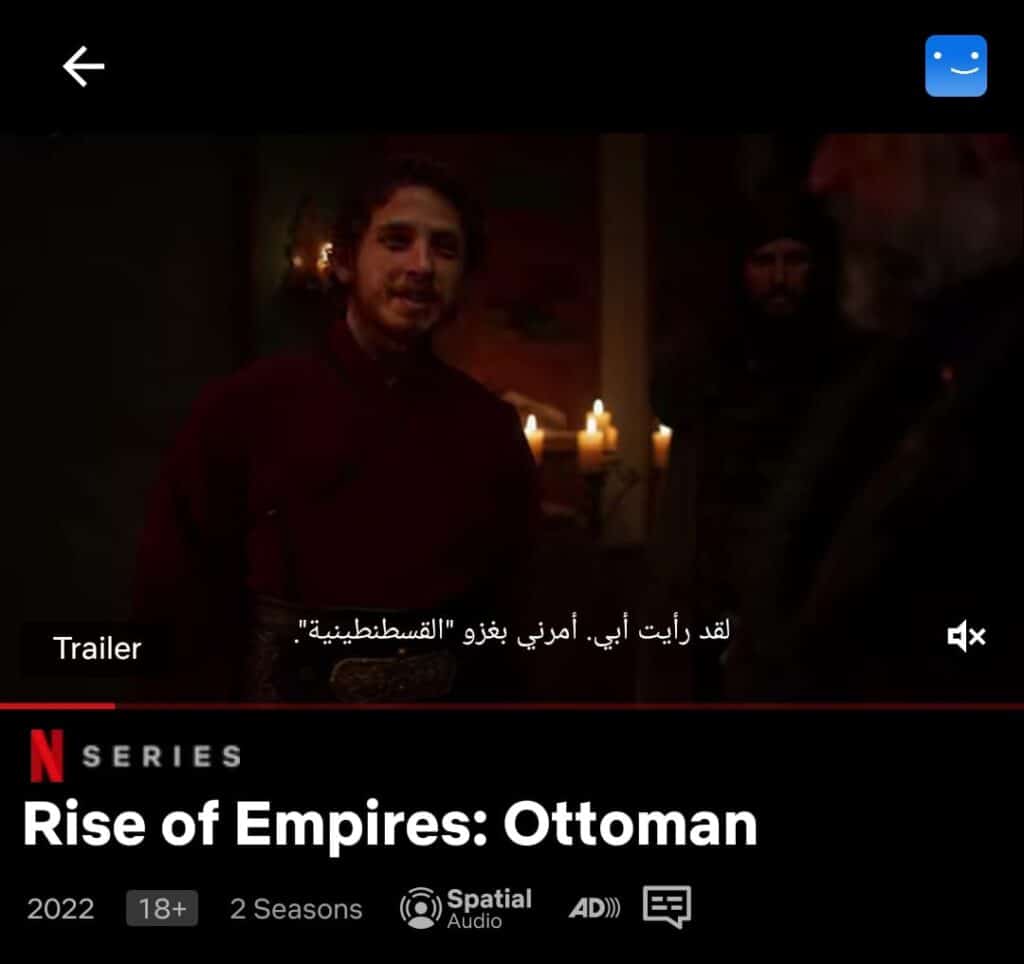
This approach makes their platform accessible to people across the globe, regardless of their language proficiency.
By embracing linguistic diversity, businesses create a seamless and engaging experience for users from different cultural backgrounds.
6. Urban, city, and rural
Segmenting based on urban, city, or rural acknowledges that urban, suburban, and rural areas have distinct consumer behaviors and lifestyles.
To effectively connect with these varied audiences, brands can customize their messaging.
A fashion brand, for instance, might recognize that urban dwellers tend to prefer sleek and modern styles, while suburban consumers might lean towards casual and comfortable fashion.
By tailoring their product offerings and marketing strategies accordingly, the brand resonates with each audience segment within a particular region, fostering a sense of relatability and understanding.
When Nike was to launch the Air Max 270, rather than setting up in the chicest parts of Paris, they headed out to the suburbs in search of the brand’s true fans.
Real-World Examples Of Geographic Segmentation
Nike:

“Nothing Beats A Londoner” video.
In this video, Nike does a great job of addressing football fans in London by including key landmarks, local football stars, and general life in London.
It worked so well that it shot to the top of YouTube’s trending chart within hours. It was even covered by national newspapers, and tweeted by London Mayor Sadiq Khan, racking up millions of views in the process.
Haribo

Haribo is one of the biggest candy brands in the world. Based in Germany,
Haribo produces most of its candy in the U.K. — but not all of it. Being an international brand, Haribo has to cater to many specific groups with different needs.
One of those groups is the population of Turkey, which is majority Muslim. That population requires food to be halal, including candy.
This means no pork is allowed, and Haribo typically uses pork gelatin in its products.
So what does Haribo do? It produces candies with beef gelatin specifically for the majority-Muslim country of Turkey.
Final Thoughts
Geographic segmentation enables brands to craft marketing strategies that resonate at a local level. By understanding the unique needs, behaviors, and preferences of consumers in different regions, companies can tailor offers, messaging, and products accordingly.
This results in greater personalization, higher conversion rates, and improved customer satisfaction. While geographic segmentation requires effort, the payoff is immense.
As evidenced by brands like Nike and McDonald’s, those who embrace location-based targeting are better positioned to capture new markets, drive sales, and build lasting connections with customers.
In today’s global landscape, geographic segmentation is no longer just a good marketing tactic – it’s a strategic imperative for success.



