We’ve all done it—bought something we didn’t plan to. Maybe it was a “limited-time” offer or a bad day that needed a quick pick-me-up. These small, emotional decisions add up quickly: impulse purchases account for nearly 40% of all online spending.
This article talks in detail about what drives impulse buying and how smart design can turn those moments of temptation into conversion.
What Is Impulse Buying (Definition + Psychology)
Impulse buying refers to making an unplanned purchase driven by emotion rather than logic. It’s that moment when desire overrides deliberation and when a shopper clicks “Add to Cart” not because they need something, but because it feels good in the moment.
Psychologists refer to this as instant gratification, the urge to satisfy a craving immediately rather than waiting. Neuroscience research indicates that dopamine, the brain chemical associated with pleasure and motivation, plays a crucial role in this process. When dopamine levels rise, people become more likely to choose immediate rewards over delayed ones, even if waiting would be a more rational choice.
In fact, a well-known study on human impulsivity found that increased dopamine activity directly heightens the tendency to make impulsive decisions—the exact mechanism behind many impulse purchases.
That’s why clicking Add to Cart can feel rewarding in the moment, even when logic says otherwise.
Impulse Buying Statistics: How Common Is It?
84% of all shoppers have made impulse purchases

This high percentage suggests a significant influence of emotional and psychological factors on spending habits, as consumers often prioritize immediate satisfaction over rational decision-making.
It also sheds light on the prevalent phenomenon of impulse buying in today’s consumer culture. Common examples of impulse purchases include clothing and groceries, with trends indicating an increase in impulse buying during special occasions, such as the holiday season. This data underscores the pervasive nature of impulse buying behavior, where individuals make unplanned and spontaneous purchases.
The prevalence of impulse buying in the market highlights the need for retailers to understand and capitalize on these tendencies, while consumers can benefit from recognizing and managing their own impulses to make more informed purchasing decisions.
40% of all the money spent on e-commerce is attributed to impulse purchases

The data highlights the substantial impact of impulsive behavior in shaping the financial dynamics of e-commerce, emphasizing the role of immediate desires and spur-of-the-moment choices in driving online sales. Managing impulse buying is crucial to save money and make more mindful purchasing decisions. Businesses in the digital marketplace can leverage this information to tailor their strategies and capitalize on the prevalence of impulse buying in the online shopping experience.
54% of U.S shoppers acknowledge spending $100 or more on impulse buys

More than half of U.S. shoppers—54 percent—have admitted to spending $100 or more on an impulse buy, including 20 percent who have spent at least $1,000. By understanding the extent to which consumers are willing to spend impulsively, businesses can optimize their approaches to capitalize on this behavior, whether through strategic promotions, targeted advertising, or creating a shopping environment that encourages spontaneous purchases.
Compulsive shopping, however, is a dangerous progression from impulse buying, with detrimental impacts on finances and personal well-being.
8 out of 10 impulse buys are made in a brick-and-mortar store

This indicates the continued significance of physical retail spaces in driving spontaneous consumer purchases. Optimizing in-store experiences and strategically placing products can be pivotal in capitalizing on impulsive buying behavior. Creating visually appealing displays, offering limited-time promotions, and ensuring an easily navigable layout can enhance the likelihood of impulse purchases.
Impulsive shopping, often driven by emotional spending, is a common behavior where people buy things to reward themselves or cope with negative feelings. Strategies to manage this behavior include undertaking a no-spend challenge.
While e-commerce continues to grow, the tangible and immediate nature of brick-and-mortar environments provides a unique opportunity for businesses to leverage human psychology and boost spontaneous buying, emphasizing the need for a well-crafted in-store strategy to complement online efforts.
Single shoppers make 45% more impulse buys compared to married shoppers.

Marketing strategies and product placements targeting single individuals may yield higher returns in terms of impulsive purchases. Understanding the distinct consumer buying behavior of single shoppers versus married ones enables businesses to tailor their promotional efforts accordingly.
Only 13% of buyers engage in planned impulse buying on a shopping trip.

While a majority of buyers may adhere to predetermined shopping lists during planned trips, the 13% engagement in impulse buying suggests that there is still room to influence purchasing decisions through targeted marketing, appealing displays, and strategic product placements.
Recognizing and capitalizing on this minority’s openness to spontaneity becomes crucial, urging businesses to craft nuanced approaches that balance the predictability of planned trips with opportunities to stimulate impulse purchases and enhance overall sales.
46% of men regret impulse buys compared to 52% of women.
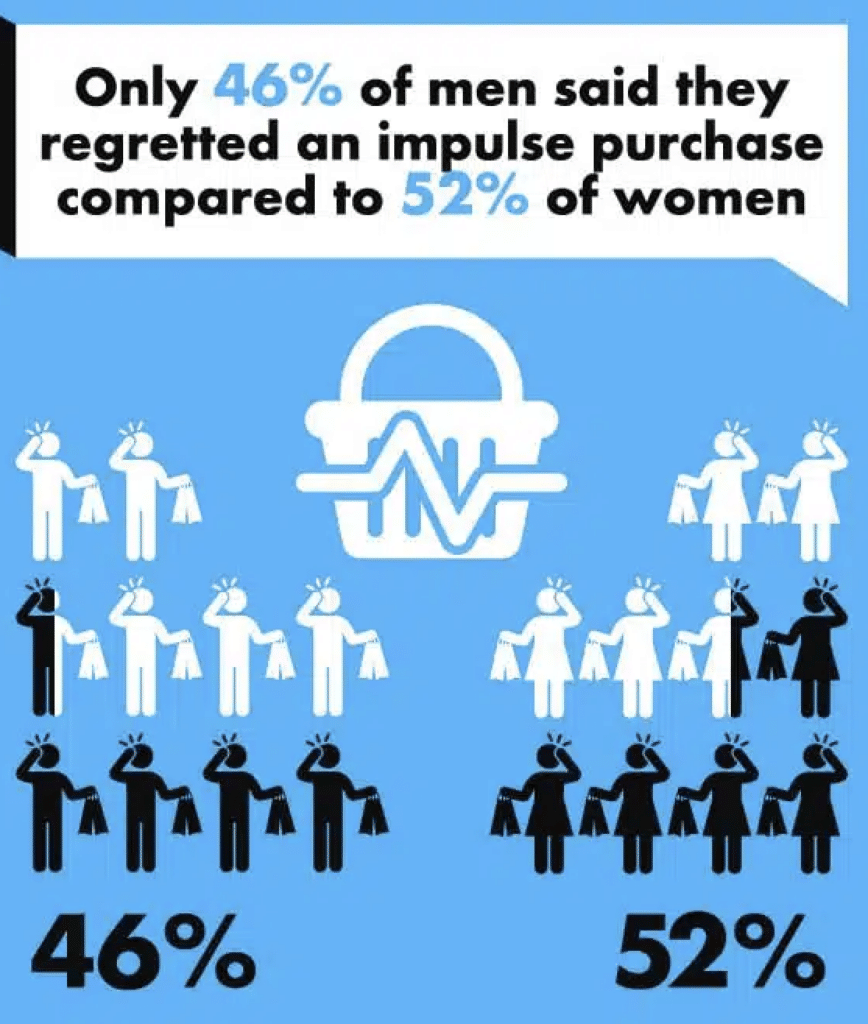
Understanding the varying degrees of post-purchase regret can inform targeted interventions, such as personalized post-purchase communication or specialized return policies, aimed at mitigating buyer’s remorse. By recognizing and responding to these gender-specific tendencies, businesses can refine their customer engagement strategies, enhance customer satisfaction, and potentially influence brand loyalty based on distinct consumer behaviors among men and women in the aftermath of impulse purchases.
52% of millennials were more likely to make impulse purchases
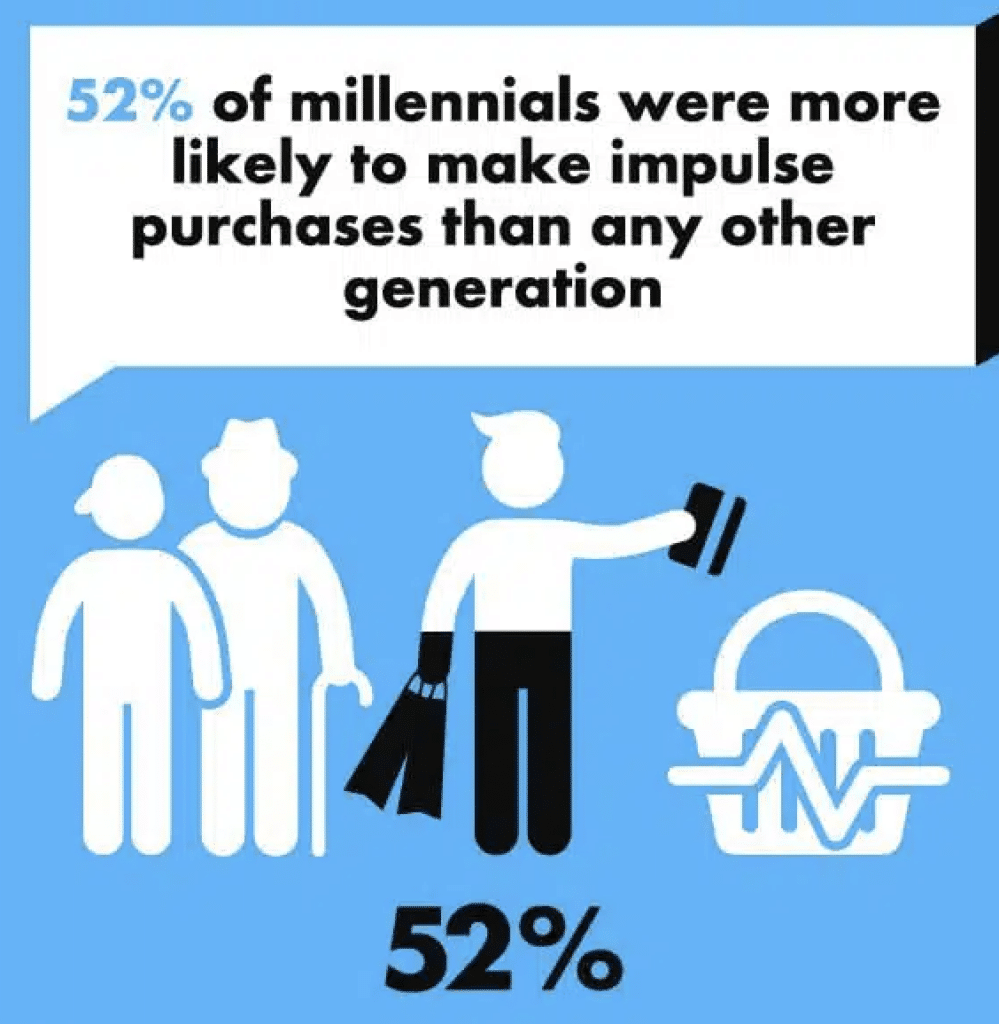
Studies show that millennials were 52% likely to engage in impulse shopping than any other generation, making it essential for businesses to understand and cater to the preferences of millennial impulse buyers.
Crafting marketing strategies that resonate with the spontaneity of their impulse spending tendencies, providing visually engaging displays, and promoting limited-time offers can capture their attention during unplanned purchases.
Recognizing the unique dynamics of millennial impulse buyers allows businesses to tailor their product offerings and promotional efforts effectively, capitalizing on the spontaneity inherent in their purchasing behavior to drive increased sales and engagement.
The average shopper will make an average of 3 unplanned purchases out of every 10 store visits they make.

All this highlights the prevalence of impulsive spending habits and impulsive buying behavior among consumers. Understanding this aspect of shopping behavior is crucial in developing effective strategies to capitalize on unplanned purchases.
Creating an in-store environment conducive to spontaneous buying, strategically placing enticing products, and leveraging promotional tactics can harness the impulse buying tendencies of customers.
Acknowledging and adapting to the frequency of unplanned purchases in the design of marketing campaigns and store layouts allows businesses to optimize their overall sales strategy, tapping into the dynamics of impulsive spending to enhance customer satisfaction and drive increased revenue.
The Psychology of Impulse Purchases
A combination of mental and emotional triggers often drives impulse purchases. Research suggests that the brain’s reward system is activated when a consumer sees a product or receives a promotional message, releasing feel-good chemicals such as dopamine. This can lead to a sense of instant gratification and pleasure, making it more likely for the consumer to make an impulse purchase.
Additionally, emotional states such as stress, anxiety, and boredom can also contribute to impulse buying. Consumers may use shopping as a coping mechanism to relieve negative emotions or to satisfy their temptation to buy. Understanding these mental and emotional triggers can help individuals develop strategies to resist impulse purchases and make more intentional purchasing decisions.
Why We Engage in Impulse Shopping
Impulse shopping is a multifaceted behavior influenced by various factors. One primary reason is the thrill of the hunt. The excitement of discovering a new product or snagging a limited-time offer can be exhilarating, leading to spontaneous purchases. Social and cultural factors also play a significant role. For instance, societal norms and peer pressure can drive individuals to make unplanned purchases to fit in or keep up with trends.
Marketing tactics are another powerful influence. Retailers use strategies like scarcity, urgency, and visually appealing displays to entice consumers into making impulse buys. The combination of these elements creates an environment where impulse shopping thrives, making it essential for consumers to be aware of these influences to manage their spending habits better.
Types of Impulse Purchases
Impulse purchases can be categorized into several types, each with its own characteristics and triggers:
- Pure Impulse Buying: This is the most spontaneous form of impulse buying, where a consumer makes an unplanned purchase without any prior intention. An example could be grabbing a candy bar at the checkout counter.
- Reminder Impulse Buying: This occurs when a consumer is reminded of a need or desire upon seeing a product. For instance, seeing a display of sunscreen might remind someone to buy it for an upcoming beach trip.
- Suggestion Impulse Buying: In this type, a consumer makes a purchase based on a suggestion or recommendation, often influenced by marketing tactics. An example could be buying a new gadget after seeing an influencer’s review.
- Planned Impulse Buying: This involves a consumer planning to make a purchase but not deciding on the specific product until they see it. For example, someone might plan to buy a gift but only choose the actual item when they find something appealing in the store.
Understanding these types of impulse purchases can help consumers recognize their buying patterns and make more informed decisions, ultimately aiding in saving money and reducing unplanned expenditures.
States of Mind When Making an Impulsive Purchase
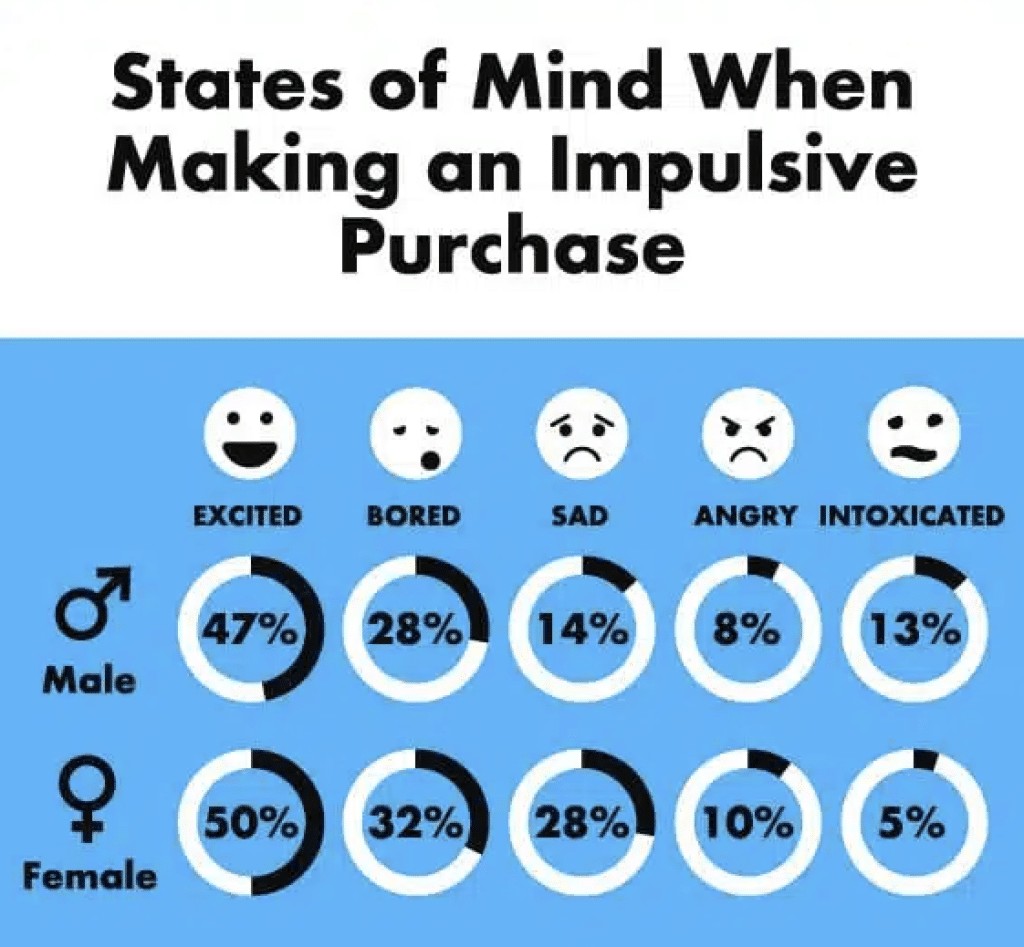
When making an unplanned purchase, 50% of females express greater excitement, whereas only 47% of males share the same level of enthusiasm.
When intoxicated, 13% of males exhibit impulse buying behavior, while only 5% of females engage in impulse purchases under the same circumstances.

Infographic by- Invesp Conversion Optimization Services


