Things would be simpler if every person who visited your website had the same ideas, dreams, and wants. You’d instantly know how to make them take action.
However, that’s not how it works.
The truth is, meeting the needs of a diverse range of desires and audience groups is tough unless you’re a major store like Amazon, Walmart, or BestBuy.
There’s a belief that if you’re a small business aiming to succeed, you should focus on a specific group and break down your audience into segments. This is where the saying ‘the riches are in the niches’ comes in.
In this article, you’ll discover:
- What market segmentation is
- 4 types of market segmentation
- Market segmentation examples
- Benefits of market segmentation.
- Case Studies on market segmentation.
Let’s get started.
What Is Market Segmentation
Market segmentation is the process of dividing a broad target market into smaller, more manageable segments based on shared characteristics, needs, or behaviors.
These segments are composed of individuals or groups that exhibit similar preferences, interests, and purchasing behaviors.
By segmenting the market, businesses can gain valuable insights into their customers, enabling them to tailor their products, services, and marketing campaigns to meet specific customer needs and preferences.
Importance of Market Segmentation
Market segmentation holds immense significance in modern business strategies, particularly in an increasingly competitive and diverse market. Here are some key reasons why it is crucial:
Customized Approach:
Understanding different customer segments’ unique needs and preferences allows businesses to create tailored marketing messages and offerings. This customization fosters a stronger connection with customers, leading to higher engagement and conversion rates.
Efficient Resource Allocation:
Market segmentation helps businesses allocate their resources more efficiently. Instead of adopting a one-size-fits-all approach, they can focus their efforts and resources on the most promising segments. This targeted strategy optimizes marketing budgets and enhances return on investment (ROI).
Improved Customer Retention:
By understanding customers on a deeper level, businesses can identify pain points and areas for improvement in their products or services. Addressing these issues leads to higher customer satisfaction, which, in turn, promotes customer loyalty and repeat business.
Competitive Advantage:
In a competitive market, a clear understanding of customer segments enables businesses to differentiate themselves effectively. By catering to specific needs and desires, they can stand out from their competitors and position themselves as the preferred choice among their target customers.
Market Expansion Opportunities:
Market segmentation allows businesses to identify untapped or underserved segments within their target market. Recognizing these opportunities can open new avenues for growth and expansion, leading to increased market share and revenue.
Effective Marketing Campaigns:
Tailoring marketing campaigns to specific segments ensures that messages resonate with the intended audience. This personalized approach garners greater attention, engagement, and a higher likelihood of conversions.
Mitigating Risk:
Businesses can reduce their reliance on a single market by diversifying their customer base across multiple segments. This diversification helps mitigate the risks associated with fluctuations in demand or changes in market conditions.
Types of Market Segmentation
Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation involves dividing customers into distinct groups based on specific demographic variables like age, gender, income, education, marital status, and more.
These attributes provide valuable insights into the characteristics and preferences of different customer segments.
Age-Based Segmentation:
Companies often use age-based demographic segmentation to target customers at different life stages.
For instance, a toy company may offer a range of products for infants and toddlers while focusing on trendy gadgets and electronics for teenagers and young adults.
See this example from Toysrus.
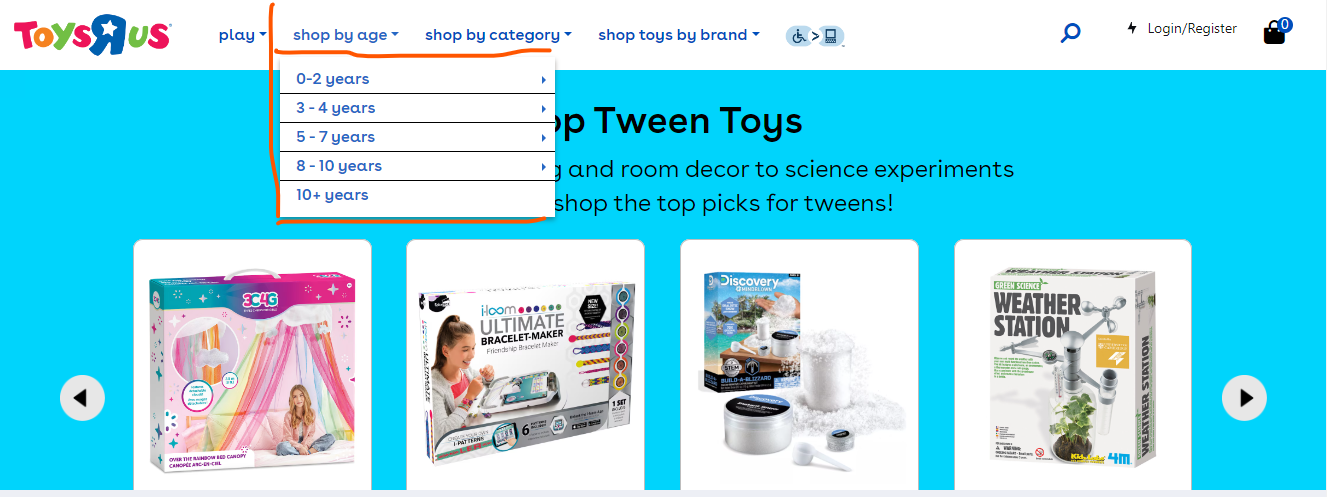
By understanding the preferences and needs of each age group, companies can develop products and marketing campaigns that resonate with their target audience.
Moreover, age-based segmentation allows businesses to effectively adapt their communication style and channels to reach each demographic.
For example, social media platforms might be more suitable for targeting younger audiences, while traditional media may be preferred for older demographics.
Gender-Based Segmentation:
Gender-based demographic segmentation is common in the fashion, cosmetics, and personal care industries. Companies tailor their products, colors, and designs to suit the preferences of men and women.
For example, a company might design masculine packaging and scents for male grooming products and use feminine aesthetics and fragrances for female-targeted products.
See this example from ASOS (the clothing retailer). This Facebook was created specifically for female customers because it features products for women. It’s shown only to female Facebook users as the chances of an average male finding this particular ad to be relevant to them is slim.
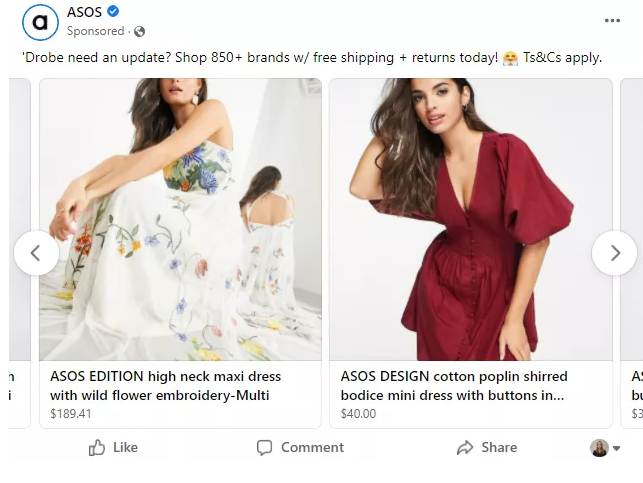
Gender-based segmentation helps businesses create a stronger emotional connection with their customers, as it aligns with their sense of identity and personal style.
Income-Based Segmentation:
Companies that offer a wide range of products at different price points often use income-based demographic segmentation.
Premium brands focus on higher-income segments and position their products as symbols of luxury and exclusivity.
See this example from Gillette:

On the other hand, companies targeting budget-conscious consumers offer more affordable options without compromising on quality.
See this example from Dollar Shave Club:

By segmenting customers based on income levels, companies can tailor their marketing messages and product offerings to match their target audience’s purchasing power and preferences.
Marital Status Segmentation:
Marital status segmentation is particularly relevant for the insurance, financial services, and travel industries.
Insurance companies might offer joint policies for married couples, while financial institutions might customize investment options based on an individual’s marital status.
For travel companies, targeting honeymoon destinations to newlyweds or single travel packages for solo travelers can be effective strategies.
Single individuals tend to prioritize themselves, while newly married couples are likely to prioritize each other and their homes.
Couples with several children have different needs than those who just had their first child. Large families might be more interested in low-cost household products, as compared to a couple with the same income but without any children.
This ad presumably targets families with small children:
Ethnicity-Based Segmentation:
Ethnicity-based demographic segmentation allows businesses to connect with customers on a cultural level.
Companies may adapt their products, advertising, and packaging to reflect the cultural preferences and traditions of specific ethnic groups.
By showing an understanding of cultural nuances, businesses can foster trust and loyalty among their target audience.
See this example from WaNaHong:
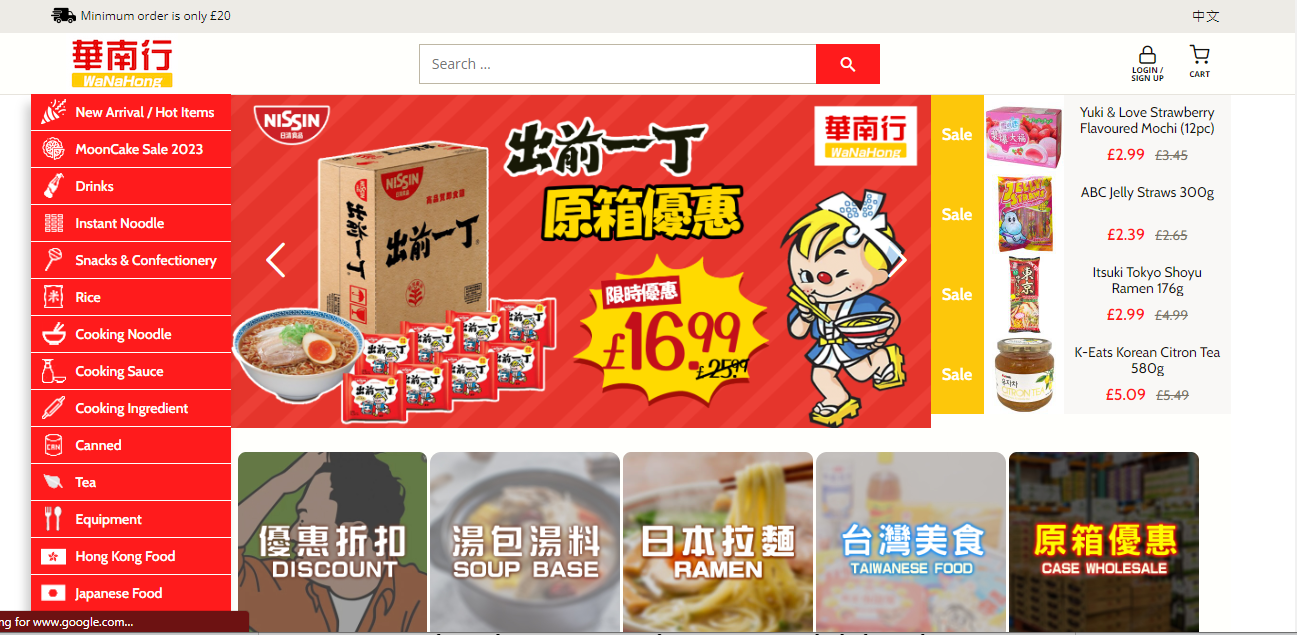
WaNaHong is an online Asian supermarket selling primarily to Asian expats living in the UK.
Their website features many familiar products from China, Japan, Taiwan, and other Asian nations and is also skewed heavily towards providing the best experience for their customers, with many headings and products described in both Chinese and English.
Geographic Segmentation
Geographic segmentation involves categorizing customers based on their physical location or regional attributes. This can include country, region, city, climate, population density, and other location-based factors.
Here are further classifications of geographic segmentation (based on how certain businesses/industries use it):
Food and Beverage Chains:
Geographic segmentation empowers food and beverage chains to cater to the diverse palates of customers in different regions.
For instance, a global coffee chain may offer regional coffee blends to match the preferences of coffee drinkers in various countries. In colder climates, they might promote hot beverages, while in warmer regions, they may focus on iced and cold brews.
Additionally, fast-food chains may adjust their menu to include local favorites or culturally relevant dishes, reflecting the culinary heritage of each region.
See this example from Oddbox (they could only deliver in London till they expanded their scope of influence):
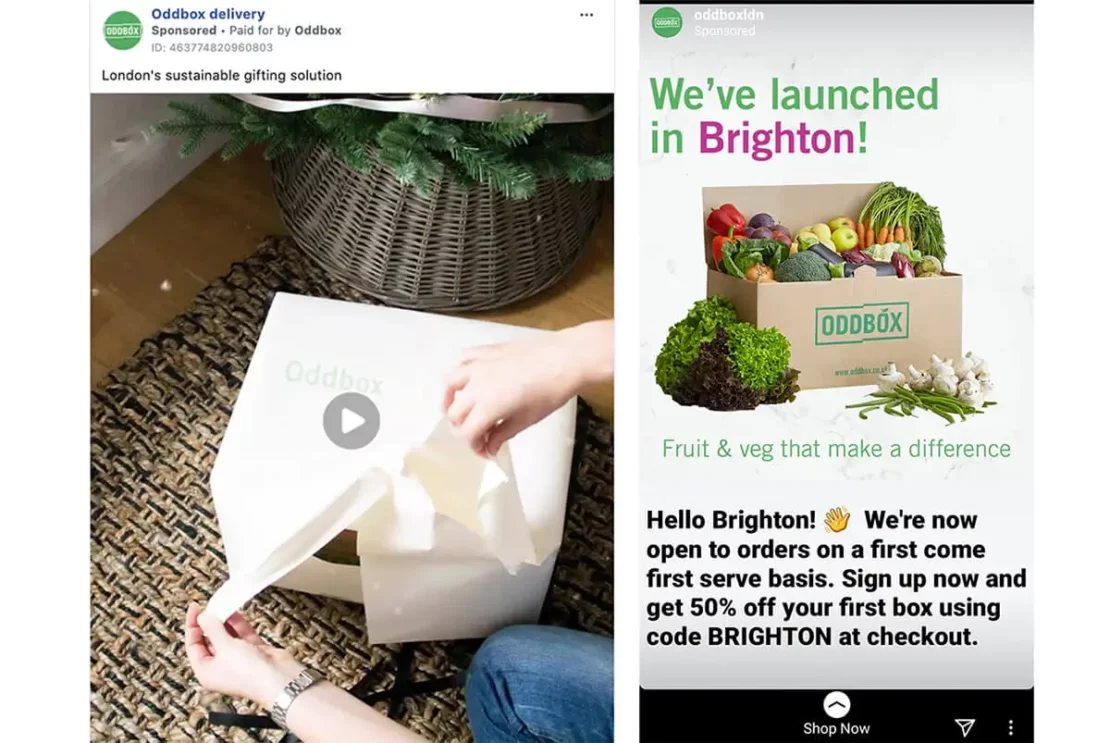
Apparel Brands:
Geographic segmentation enables apparel brands to address seasonal variations and climate differences.
A clothing retailer with a presence in multiple countries may customize its clothing lines based on local weather patterns.
In colder regions, they might offer heavy winter coats and accessories; in tropical areas, they might prioritize lightweight and breathable fabrics suitable for hot weather.
By considering climate-specific needs, they optimize customer satisfaction and demand.
See this example from ASDA:

The beginning of April 2014 saw ASDA’s clothing brand George launch its summer campaign,’ Real Summer Days.’
In response to the notoriously changeable British weather, ASDA created a weather-triggered landing page for their online store, which displayed personalized product recommendations based on the visitor’s local weather.
Tourism and Hospitality Industry:
Tourism and hospitality business leverage geographic segmentation to create targeted marketing campaigns. They may tailor vacation packages and promotions to appeal to specific regional preferences.
For example, a travel agency might promote beach getaways during winter months in colder regions, enticing customers to escape to warmer destinations.
Alternatively, they might highlight cultural tours and historical sites for travelers interested in exploring heritage-rich locations.
TUI, previously known as Thomson Holidays, wanted to increase holiday bookings by driving more quality traffic to their website.
TUI partnered with a weather website, implementing a brand takeover of both desktop and mobile app properties.
When users experienced rainy, cloudy, snowy, or cold weather, they were shown creative executions of ‘sun and sea’ holiday destinations designed to create consumer desire.
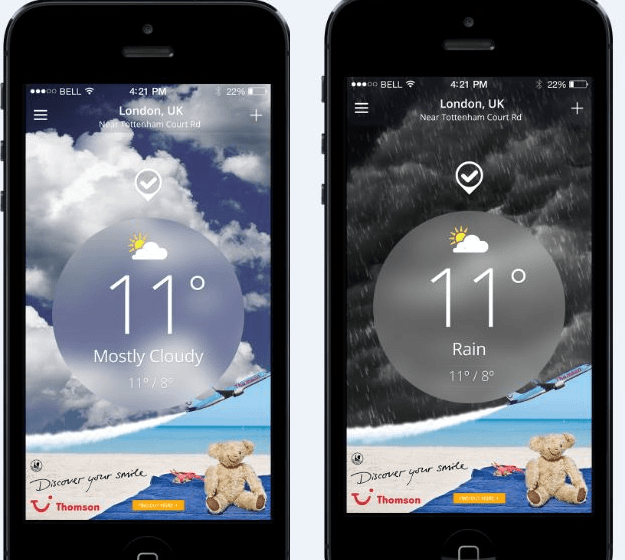
Real estate Developers
Real estate companies utilize geographic segmentation to target potential buyers based on location-specific features.
They may emphasize the availability of large yards and family-friendly amenities in suburban developments, catering to the needs of families and individuals seeking a tranquil living environment.
In contrast, they might market urban properties based on their proximity to entertainment hubs, nightlife, and cultural attractions, appealing to younger and more socially active demographics.
Automotive Industry:
Car manufacturers and dealerships leverage geographic segmentation to adapt their marketing approaches for different vehicle models.
In regions with rough terrain or inclement weather, they may promote SUVs and all-wheel-drive vehicles, highlighting their performance in challenging conditions. In areas with a strong interest in sustainability, they might emphasize electric or hybrid vehicles to align with the region’s environmental values.
Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation involves segmenting customers based on their lifestyle, values, beliefs, interests, personality traits, and other psychological factors. This approach delves into the emotional and psychological aspects that influence consumer behavior.
Let’s consider a fitness apparel company that wants to develop a marketing campaign to promote its new line of activewear targeted at fitness enthusiasts.
To create emotionally resonant marketing messages, they employ psychographic segmentation to understand their target audience’s lifestyle, values, beliefs, interests, and personality traits.
Identifying the Target Audience:
The company begins by identifying its target audience as fitness enthusiasts who are passionate about leading a healthy and active lifestyle. They want to understand what motivates this group beyond just their fitness goals.
Creating Buyer Personas:
Next, the company develops detailed buyer personas for their target audience. They conduct surveys, and interviews, and monitor social media to gain insights into customers’ habits and preferences.
They might discover that their target audience includes gym-goers, outdoor adventurers, yoga enthusiasts, and individuals who prioritize overall well-being.
Understanding Lifestyle and Interests:
Through psychographic segmentation, the company uncovers that its target audience values adventure, self-improvement, and community.
They participate in activities like hiking, rock climbing, and group fitness classes. The company realizes that its customers’ motivation to stay fit is driven by physical health, the desire for personal growth, and a sense of belonging to a supportive fitness community.
Crafting Emotionally Resonant Messages:
With a deeper understanding of their target audience’s psychographic traits, the company creates emotionally resonant marketing messages that align with their customers’ values and interests.
Instead of solely focusing on product features, the messages emphasize the emotional benefits of activewear.
For example, they might emphasize how activewear empowers wearers to conquer new fitness challenges, connect with like-minded individuals, and feel confident in their journey to self-improvement.
Using Storytelling and Visuals:
The company uses storytelling and compelling visuals in its marketing materials to evoke emotions that resonate with its target audience.
They might showcase stories of real customers achieving their fitness goals or exploring breathtaking outdoor locations in activewear. These stories create an emotional connection with potential customers, making them feel inspired and motivated to be a part of the brand’s fitness community.
Personalizing Communication:
Using psychographic insights, the company tailors its communication to different segments within its target audience.
For example, they might send personalized emails featuring content related to outdoor adventures to customers who have shown an interest in hiking while providing yoga-related content to those interested in mindfulness practices.
This customization enhances engagement and reinforces the brand’s understanding of individual customer needs.
Engaging on Social Media:
The fitness apparel company actively engages with its target audience on social media platforms. They create and share content that aligns with their customers’ interests and values.
This includes fitness challenges, motivational quotes, and user-generated content showcasing the activewear used in various fitness activities.
Engaging with customers on social media fosters a sense of community, strengthening the emotional bond between the brand and its audience.
Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation involves segmenting customers based on their past behaviors, actions, and interactions with a brand. This includes purchase history, brand engagement, website interactions, loyalty, and more.
Here’s how some top brands use behavioral segmentation:
Amazon:
Amazon, the e-commerce giant, is a prime example of a company that uses behavioral segmentation to personalize product recommendations.
Through sophisticated algorithms, Amazon analyzes customers’ browsing and purchase history to understand their preferences and interests.
Based on this data, Amazon suggests relevant products that align with each customer’s past behavior.
For instance, if a customer frequently purchases books on a particular topic, Amazon may recommend related books or products in that category.
This personalized approach enhances the customer shopping experience and increases the likelihood of repeat purchases.
I’ve been wanting to get more office accessories; look at what my Amazon recommendation looks like.
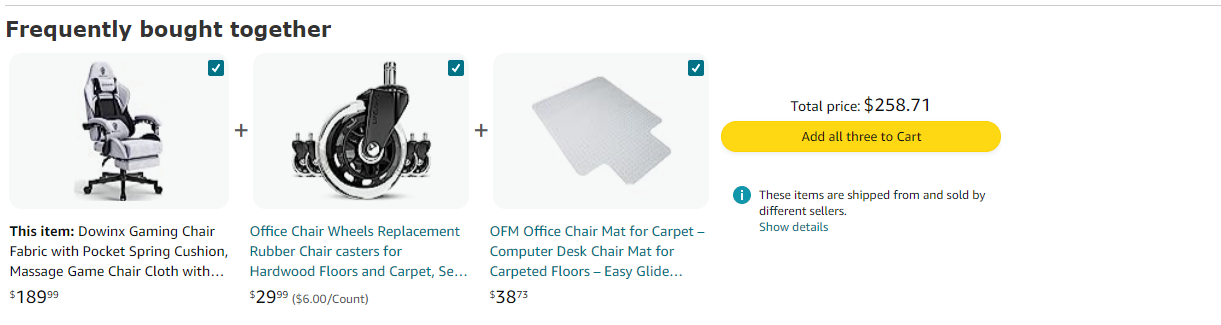
Netflix:
Netflix, the streaming service, utilizes behavioral segmentation to personalize content recommendations for its users.
By analyzing viewing history, movie ratings, and interactions with different genres, Netflix tailors its content suggestions to align with each viewer’s preferences.
Here’s what my Netflix recommendations look like:
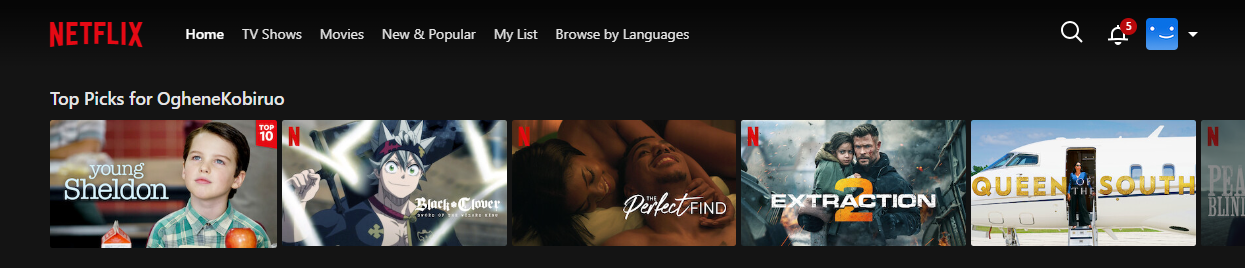
Starbucks Rewards Program:
Starbucks, the coffee chain, leverages behavioral segmentation through its rewards program.
The program tracks customers’ purchase behavior and spending patterns. Based on their past purchases, Starbucks offers personalized rewards and promotions.
For instance, a customer who frequently buys a particular drink may receive a special offer for that specific beverage. This approach incentivizes repeat visits and strengthens customer loyalty by providing rewards that align with individual preferences.
Spotify:
The music streaming service Spotify uses behavioral segmentation to create personalized playlists and song recommendations.
By analyzing users’ listening history, liked songs, and created playlists, Spotify generates “Discover Weekly” and “Daily Mix” playlists with songs tailored to each user’s musical tastes.
This personalized music discovery feature encourages users to spend more time on the platform and reinforces their connection with the service.
Here’s what a sample of my Spotify recommendation looks like:
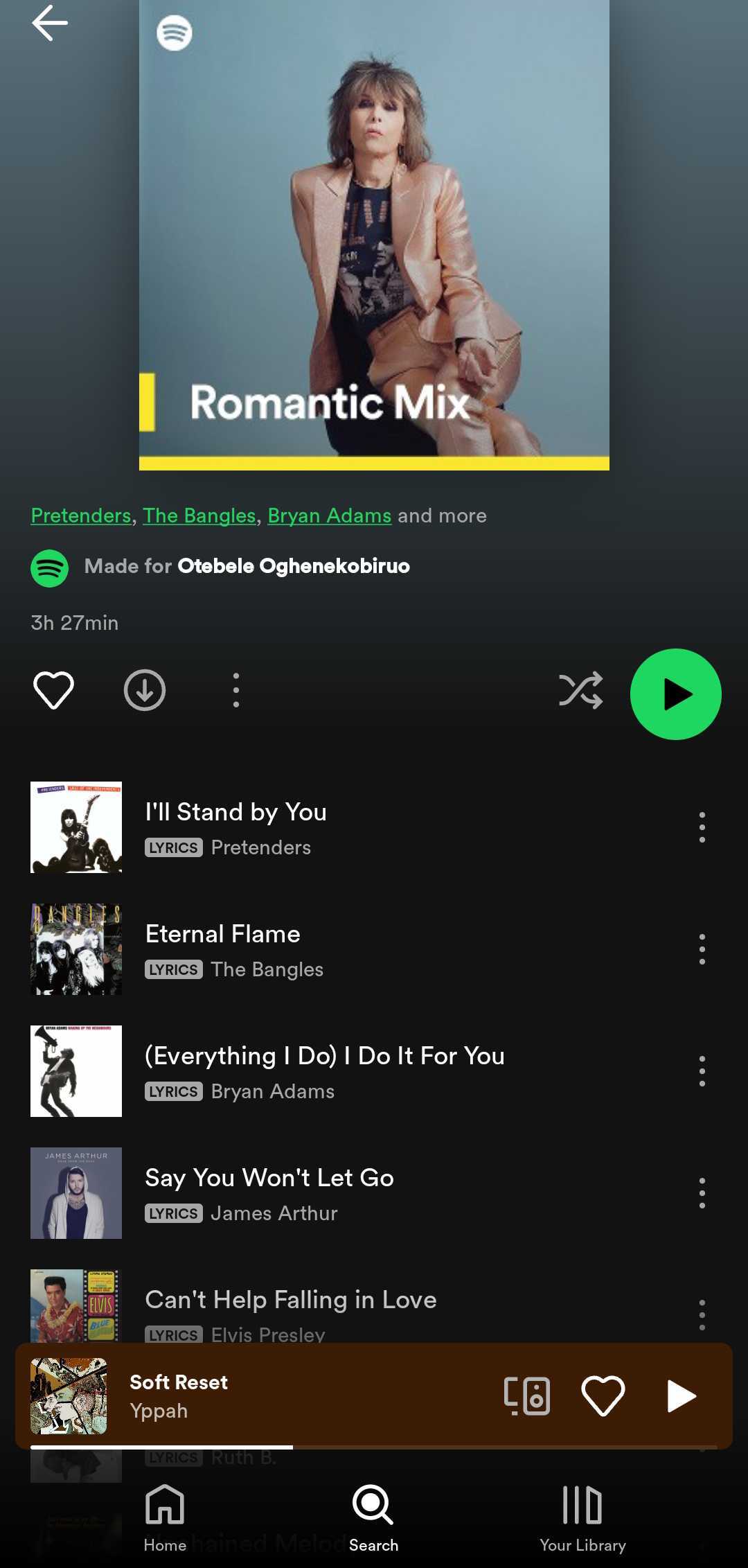
Sephora:
Sephora, the beauty retailer, employs behavioral segmentation to offer personalized beauty product recommendations.
Sephora’s loyalty program, Beauty Insider, provides tailored product suggestions and exclusive offers by tracking customers’ past purchases and preferences.
Customers receive recommendations based on their skincare concerns, makeup preferences, and beauty brands they have shown an interest in. This personalized approach enhances the shopping experience and encourages brand loyalty.
Implementing Market Segmentation
1. Surveys, Feedback, and Social Media Monitoring
Surveys:
Surveys are valuable data collection tools that allow businesses to gather structured information from their target audience.
Companies can design online questionnaires to capture customer preferences, opinions, and satisfaction levels. By asking specific and relevant questions, businesses can obtain quantitative data that can be analyzed to identify trends and patterns among different customer segments.
Surveys can be distributed through email campaigns, website pop-ups, or social media ads to reach a wide audience and collect data efficiently.
A tool you can use here is Figpii.
Feedback Forms:
Feedback forms provide businesses with qualitative insights into customer experiences and sentiments. These forms can be embedded on websites or emailed after a customer interacts with the company.
Open-ended questions in feedback forms enable customers to provide detailed feedback, suggestions, and grievances, helping businesses understand the emotions and motivations behind their actions.
SurveyMonkey is a tool you can use here:
Social Media Monitoring:
Social media platforms serve as valuable sources of customer data. By monitoring mentions, comments, and discussions related to their brand, businesses can gain real-time insights into customer sentiments, interests, and trends.
Social media listening tools analyze this unstructured data, allowing companies to identify emerging topics, track brand reputation, and respond to customer inquiries promptly.
BrandWatch is a tool you can use here:
2. Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data analytics plays a pivotal role in transforming raw data into actionable insights.
Businesses can identify patterns and trends within customer data through various statistical methods and visualization techniques.
For example, they may discover that customers from a specific region prefer certain product features or identify a correlation between customer satisfaction and repeat purchases.
These insights guide businesses in making informed decisions about segmentation and marketing strategies.
Data analytics goes beyond straightforward observations and can uncover hidden insights that might not be immediately apparent. Using advanced analytics tools, businesses can conduct clustering, market basket, or sentiment analyses to identify underlying trends or associations.
For instance, a retailer may discover that customers who purchase certain items together belong to a distinct segment with specific lifestyle preferences.
Such insights empower businesses to create targeted marketing messages and product offerings that cater to these hidden segments.
Rapidminer is a tool you can use for data analysis:
3. Targeting and Positioning Strategies
Businesses can identify high-potential target segments through data analysis based on relevance and size.
This involves identifying segments that align closely with the company’s offerings, have significant purchasing power, and show growth potential.
For example, an outdoor adventure gear company may discover that the “enthusiastic hikers” segment has been growing steadily and has a high spending capacity, making it a high-potential target segment for its marketing efforts.
Customer personas are fictional characters that represent target segments based on data-driven insights. They add a human touch to the segmentation process by giving these segments identifiable traits, motivations, and aspirations.
For instance, a persona for the “health-conscious urban professionals” segment may include details about their fitness goals, work-life balance, and preferences for organic products. Creating personas helps marketing teams empathize with customers, leading to more relatable and emotionally resonant communication.
To ensure personas align effectively with target segments, businesses should base them on accurate and up-to-date data.
Regularly update personas with new customer insights to reflect customer behavior or preferences changes.
Additionally, the persona creation process, involve key stakeholders, such as sales representatives and customer service teams. Their input and on-the-ground experience can provide valuable perspectives on customer needs and challenges.
By aligning personas with target segments, businesses can create tailored marketing messages that address specific pain points and aspirations, fostering a stronger connection with customers.
Case Studies: Successful Market Segmentation Strategies
Coca-Cola: Share A Coke Campaign

The “Share a Coke” campaign was first launched by Coca-Cola in Australia in 2012 and then in the UK in 2013 to increase sales and engage customers, especially millennials who value individuality and personalization.
It involved personalized Coke bottles printed with common names and encouragement to “share a Coke” and your experience on social media.
By doing so, Coca-Cola targeted the millennial generation. It was a multichannel campaign involving TV, billboards, SMS, and especially social media like Facebook.
Users could customize bottles with friends’ names and share their names lit up on the iconic Coke sign in Sydney. This drove high engagement on social media, with large amounts of user-generated content using the #shareacoke hashtag.
The results showed increases in youth consumption, media impressions, social media engagement, custom bottles printed and shared, and an improved, positive brand image.
The reasons for its success were its personal connection with consumers, the powerful “Share a Coke” call-to-action and the continuous updating of the campaign.
Vans

Vans is an American shoe manufacturer founded in 1966 that made the bold decision to champion alternative subcultures such as skateboarding and bicycle motocross (BMX).
The brand appealed to so-called “misfits and rebels” who saw these sports as a hobby or passion and a lifestyle choice.
Vans are now taking advantage of the athleisure trend target market and have a much broader appeal, but the company’s stores continue their retro, skateboarding vibe.
In a Manhattan store, for example, vintage posters of skateboarders adorn the walls with industry slogans and skateboards from popular brands.
Next to skateboard accessories such as wheels and trucks is apparel more reminiscent of earlier decades, with muted colors and oversized logos.
Final Thoughts
To win in your niche/industry, you need to identify your ICP and which demography they fit into. Doing this goes a long way to give you several options by which you can run campaigns and improve your conversions



